Figure 2.
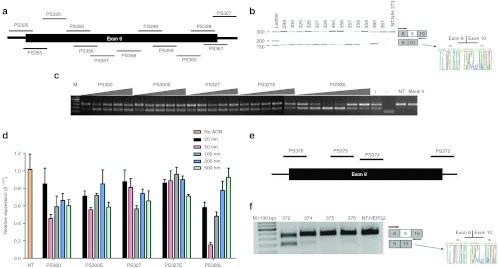
Effect of AONs on mouse and human IL-1RAcP pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. (a) AONs targeted to mouse IL-1RAcP pre-mRNA exon 9 and exon-intron junctions. (b) Test of AONs on NIH-3T3 cells at 500 nmol/l concentration for 24 hours. RT-PCR analysis of samples shows the full-length upper band and the skipped product as a lower band that were amplified with primers specific for exon 8 and 10. Sequence analysis also confirmed exon 9 skipping. (c) RT-PCR results of RNA samples from NIH-3T3 cells transfected with AONs PS300, PS327, 25-mer counterparts of them and PS300L that was designed to increase efficiency of PS300. Triangles show increasing concentrations of 20, 50, 100, 200 and 500 nmol/l for full 2′-O-MePS oligos and additional 10 nmol/l for PS300L (+ = positive control PS300, 100 nmol/l; − = water control, NT = non-transfected cells, Mock tr = only Lipofectamine-2000). (d) Quantification of skipping levels of AON concentration from 20 to 500 nmol/l by qPCR analysis. β-Actin was used as the reference gene and each bar represents the mean value of three different experiments ± SEM. (e) AONs targeted to human IL-1RAcP pre-mRNA exon 9 and exon-intron junctions. (f) Test of AONs on HEPG2 cells at 500 nmol/l for 24 hours. RT-PCR analysis of samples shows the full-length upper band and the skipped product as a lower band that were amplified with exon 8- and 10-specific primers. The sequence analysis also confirmed exon 9 skipping. AON, antisense oligonucleotide; IL-1RAcP, interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein; qPCR, quantitative PCR; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-PCR.
