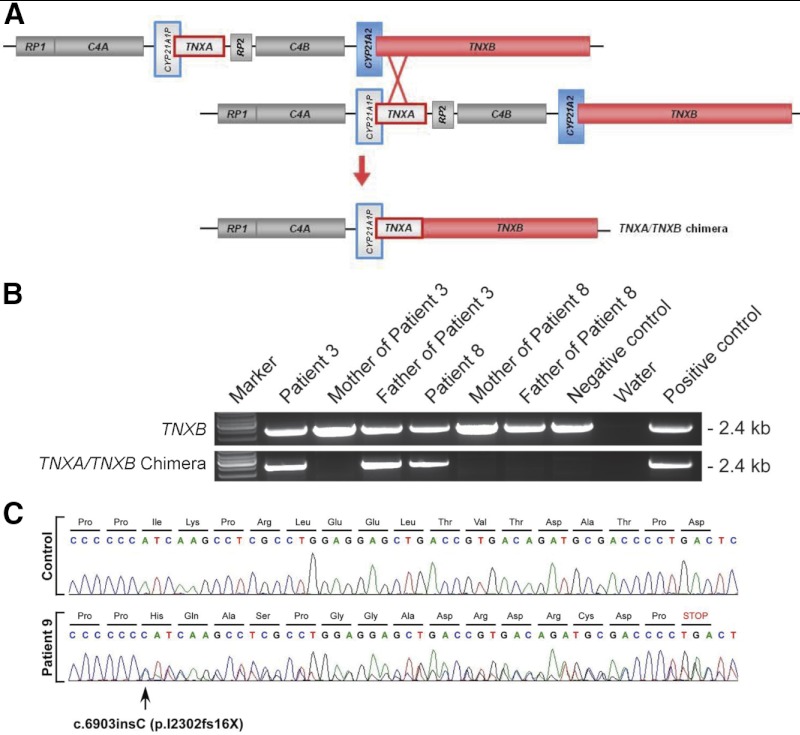
Figure 1.
Mutation analysis of the TNXB gene in CAH-X patients. A, Schematic of the tenascin genes undergoing unequal crossover during meiosis resulting in a TNXA/TNXB chimera. CYP21A2 encodes the active 21-hydroxylase gene (blue); and TNXB encodes the active tenascin gene (red). Pseudogenes CYP21A1P and TNXA are in gray and are framed with the color of the corresponding functional gene. RP1 encodes a serine/threonine nuclear kinase gene (gray), and RP2 encodes the corresponding truncated pseudogene (gray). C4 encodes the fourth component of serum complement gene (gray). B, PCR-based identification of TNXA/TNXB chimera. Patient 8 is de novo. Negative control is a patient with intact CYP21A2 and TNXB genes. Positive control is a published carrier of TNXA/TNXB (13). C, TNXB sequencing chromatogram showing a heterozygous single-nucleotide insertion.