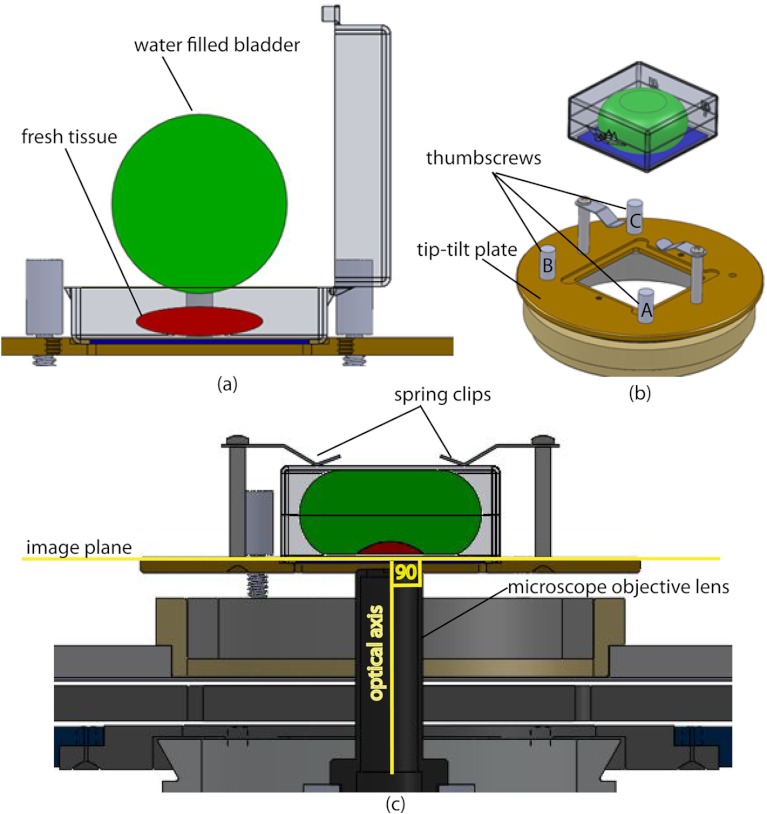
Fig. 4.
Schematic representation of the tissue-flattening device: (a) 2-D view of the tissue (in red) inside the cassette in its natural shape, as often seen in Mohs surgical excisions, with the edges curved up from the image plane and the lower (to be imaged) surface not flattened. The cassette is shown to be open with no force is applied to the water-filled bladder; (b) view of the closed tissue-cassette before mounting on the tip-tilt plate; the thumbscrews A, B, and C can be used to adjust the tip and tilt of the image plane relative to the optical axis, so as to orient the two at exactly 90 deg to each other; (c) schematic representation shows how the tissue is flattened, relative to the image plane and optical axis, by the water filled bladder when force is applied to it.