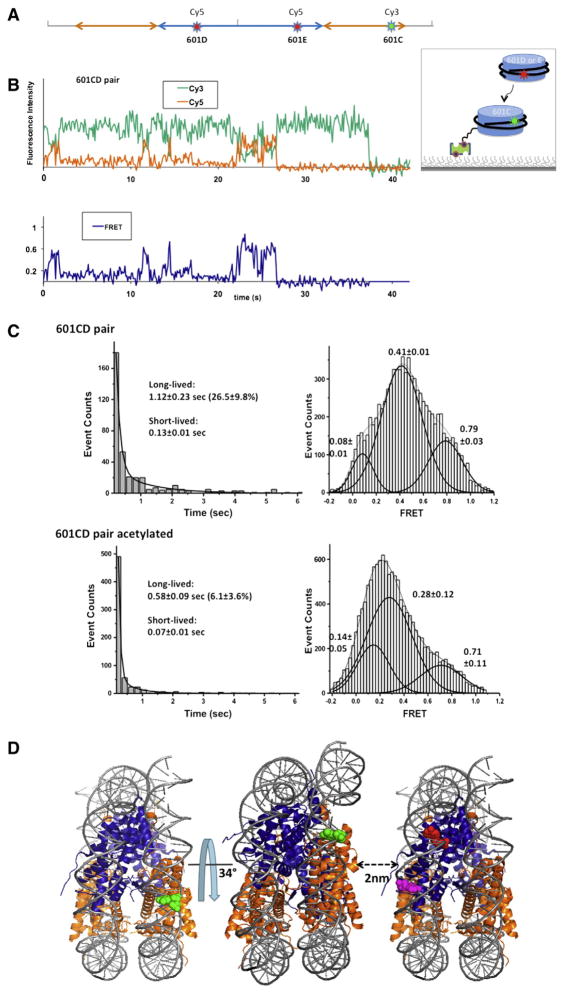
Fig. 3.
Effects of histone acetylation on internucleosomal interactions. A. Schematic representation of fluorophore positions on a 601 DNA fragment to study nucleosome interactions [13]. Each nucleosome is assembled with a fluorophore, either Cy3 or Cy5. Cy3 labeled 601C nucleosomes were immobilized on a surface and Cy5 labeled 601D nucleosomes or 601E nucleosomes were injected to the sample chamber [13]. B. A typical FRET time trace revealing the spontaneous formation of dinucleosomes between 601C and 601D nucleosomes [13]. C. Lifetime histograms of the dinucleosomal states were constructed, which revealed a long-lived and a short-lived population. The long-lived dinucleosomal states were collected in the FRET time traces and histograms of their FRET efficiencies were constructed to reveal that there is a overall decrease in the FRET efficiency upon the acetylation [13]. D. Schematic representation of the most compact dinucleosomal state modeled with the crystal structure of a nucleosome core particle (3MVD) [13].