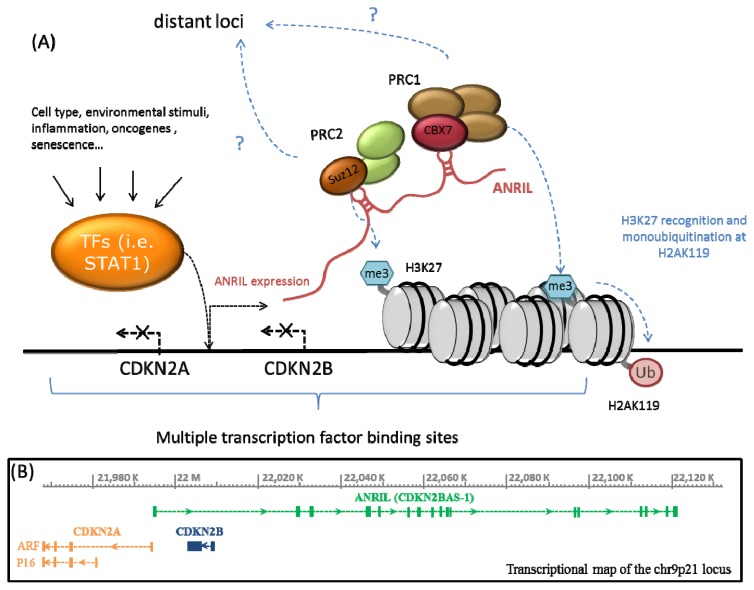
Figure 1.
(A) Chr9p21 region is rich in regulatory elements and several transcription factor (TF) binding sites have been predicted along its sequence. These transcription factors are activated in response to external factors and signaling pathways, in a cell-type specific manner. TF binding possibly activates or represses the expression of ANRIL. Polycomb protein complexes 1 and 2 (PRC1 and PRC2), have RNA binding domains in their subunits CBX7 and SUZ12 respectively. ANRIL binds SUZ12 subunit of PRC2 to induce methylation of histone 3 in the lysine 27 (H3K27) and consequent silencing of the CDKN2A/B locus. ANRIL binds CBX7 in PRC1 which allows the recognition of H3K27 necessary for the monoubiquitination at histone 2A at lysine 119 (H2AK119) and maintenance of silencing. Therefore, ANRIL modulation impacts in the repressing ability of Polycomb proteins, inducing or inhibiting expression of CDKN2A/B and possibly other distant loci by histone modification. The disease-associated alleles might impair TF binding and response to different stimuli, alter ANRIL/CDKN2A/B expression (and possibly other loci) and contribute to disease development and progression; (B) Diagram showing the transcripts encoded in the 9p21 locus. ANRIL is represented in the diagram as the longest variant reported (CDKN2BAS-1), but several other alternative isoforms have been described.