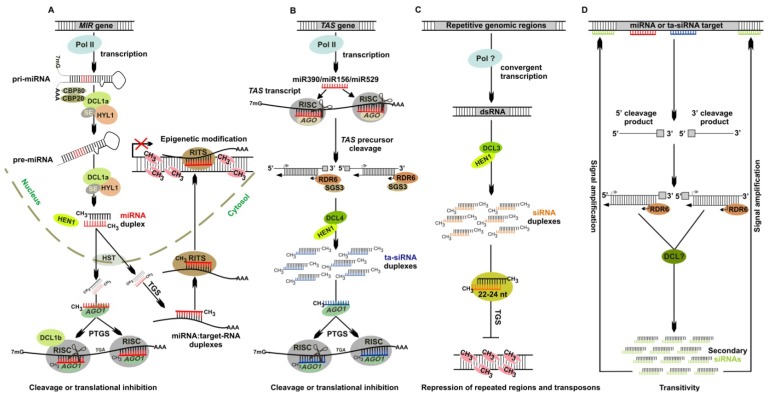
Figure 1.
Different endogenous small interfering RNA (siRNA) pathways of P. patens. Only PpDCLs and PpRDR6 have been functionally characterized in P. patens; evidence for proteins shown in figure comes from Arabidopsis and their homologous exist in P. patens. (A) P. patens miRNA pathway. MIR genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II into pri-miRNA transcripts that are further processed into pre-miRNAs harboring a characteristic hairpin structure. From the stem of the pre-miRNA the miRNA/miRNA* duplex is excised by PpDCL1a and can be assisted by HYL and SE proteins. These are then methylated by HUA ENHANCER 1 (HEN1) and transported to the cytoplasm by HASTY (HST). The miRNA guide strand is selected, incorporated, and stabilized in dedicated AGO1 protein. miRNA-guided AGO1-containing RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) directs mRNA cleavage or translation inhibition of the target transcript. Highly abundant miRNAs are either loaded into a RITS complex and subsequently interact with their target to form a duplex, or these duplexes are formed at first and then loaded into RITS. The miRNA:RNA duplexes bound by RNAi-induced transcriptional silencing complex (RITS) initiate DNA methylation at complementary genomic loci. (B) P. patens ta-siRNA pathway. TAS genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II into TAS precursors harbouring miR390, miR156 and miR529 binding sites. After TAS precursor cleavage at these miRNA sites the middle cleavage product is converted into double-stranded RNAs (dsRNA) by PpRDR6 and subsequently processed into phased ta-siRNAs by PpDCL4. ta-siRNAs are loaded into RISC where they act like miRNAs. (C) P. patens siRNA pathway from repetitive genomic regions primarily LTR-retrotransposons and helitron DNA transposons. dsRNA processed into siRNAs by PpDCL3 and HEN1-mediated siRNA stabilization, the PpDCL3-dependent 22–24 nt siRNAs caused a de-repression of LTR retrotransposon-associated reverse transcriptases pointing to an epigenetic control of these elements. (D) Secondary siRNAs in P. patens. dsRNA is synthesised from cleaved miRNA or ta-siRNA targets by RdRP and processed into secondary siRNAs that mediate cleavage of the target RNA upstream and downstream of the miRNA/ta-siRNA recognition motif resulting in an amplification of the initial small RNA trigger.