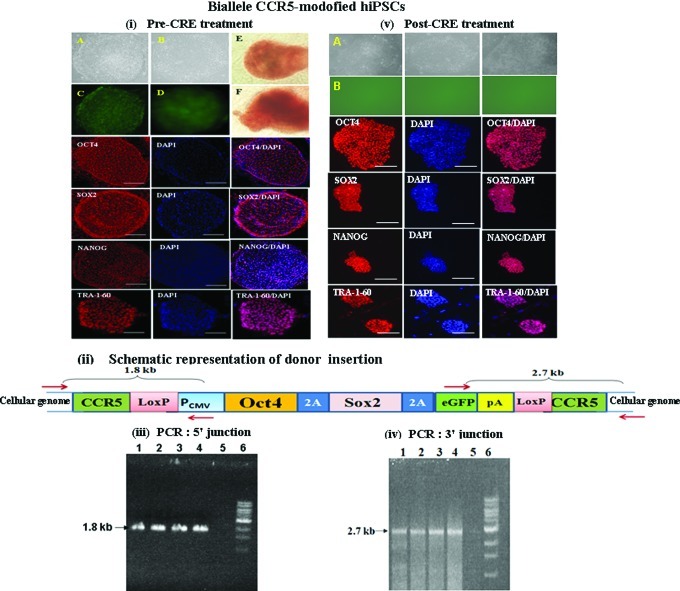
FIG. 3.
Characterization of biallele CCR5-modified hiPSCs, generated from human fibroblasts by targeted insertion of Oct4/Sox2 transcription factors at the CCR5 locus, using CCR5-specific ZFNs. (i) Morphology of biallele CCR5-modified hiPSCs, before CRE treatment. (A, B) Bright field images of the morphology 2 representative biallele CCR5-modified hiPSC colonies. (C, D) eGFP fluorescence images of hiPSC single-cell colonies shown in (A, B). (E, F) Alkaline phosphatase staining of 2 biallele CCR5-modified hiPSC lines. Immunostaining for Oct4/Sox2/Nanog/Tra1-60 and DAPI staining of biallele CCR5-modified hiPSCs are shown. (ii) Schematic representation of donor (Oct4/Sox2/eGFP flanked by CCR5 homology arms) insertion site at the CCR5 locus of single-allele CCR5-modified hiPSCs. PCR primers anchored outside the CCR5 homology arms and primers anchored inside the donor for 5′ and 3′ junction sites are shown. pA denotes polyA sequence. (iii) PCR analysis of 5′ junction of donor insertion site in 4 different biallele CCR5-modified hiPSC lines, before CRE treatment. Lanes: 1–4, biallele CCR5-modified hiPSC lines; 5, control IMR90 cells; and 6, 1 kb ladder. PCR analysis yields the expected band size (1.8 kb) confirming insertion of the donor at the CCR5 locus. (iv) PCR analysis of 3′ junction of donor insertion site in 4 different biallele CCR5-modified hiPSC single-cell colonies, before CRE treatment. Lanes: 1–4, single-allele CCR5-modified hiPSC colonies; 5, control IMR90 cells; and 6, 1 kb ladder. PCR analysis yields the expected band size (2.7 kb) confirming insertion of the donor at the CCR5 locus. (v) Morphology of biallele CCR5-modified hiPSCs, post Cre treatment. (A) Bright field images of the morphology 3 representative biallele CCR5-modified hiPSC lines generated, post Cre treatment. (B) eGFP fluorescence images of the IMR90 hiPSC lines shown in A. Immunostaining for Oct4/Sox2/Nanog/Tra1-60 and DAPI staining of the hiPSC lines are also shown. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd