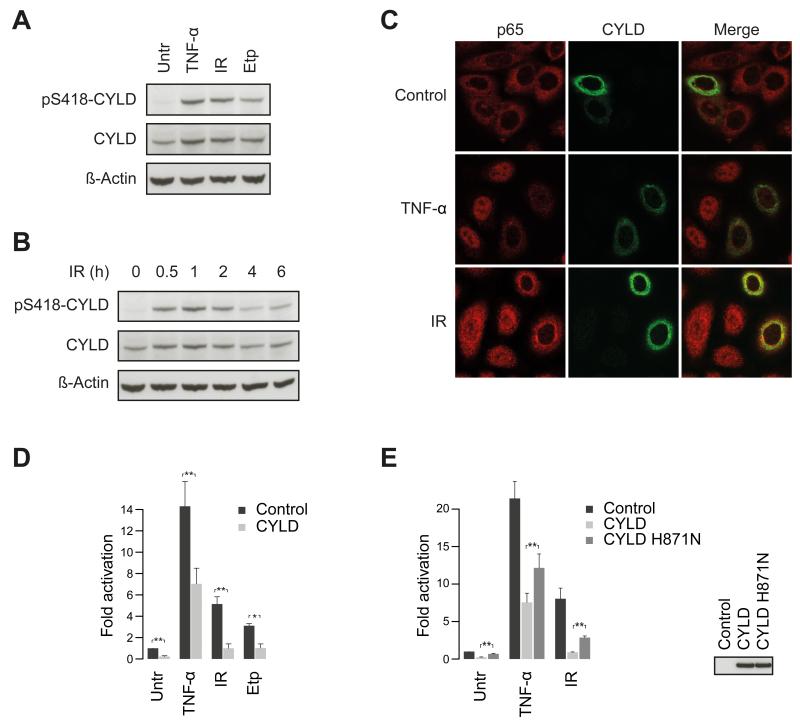
Figure 4.
CYLD regulates DNA damage-induced activation of NF-κB signaling. (A) Phosphorylation of CYLD Ser-418 by DNA damage inducing agents. Cells were treated with TNF-α, IR, or etoposide (Etp) and phosphorylation was analyzed using Ser-418 phospho-specific CYLD antibody. (B) Dynamics of DDR-induced CYLD phosphorylation. Cells were irradiated and allowed to recover for the indicated time points, and phosphorylation was detected as described above. (C) CYLD inhibits nuclear translocation of the p65 subunit of NF-κB. Cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding CYLD and nuclear translocation of p65 was analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy after treatment with TNF-α or IR. (D and E) CYLD inhibits DNA damage-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity. Cells were transfected with the indicated CYLD constructs or empty vector and NF-κB activation was monitored with luciferase-based reporter assays. Error bars specify the standard deviation of the three independently performed experiments. p**<0.05. (See also Figure S5)