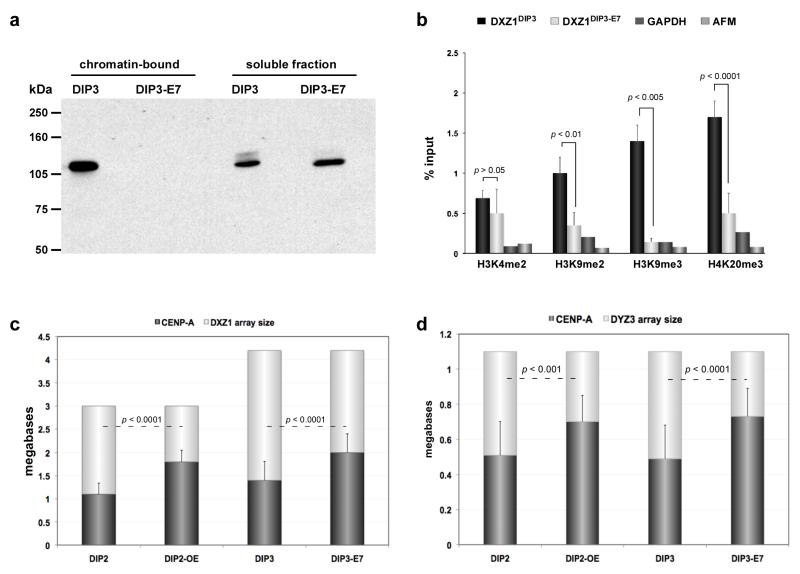
Figure 5. CENP-A domains size changes in response to protein dosage.
(a) Primary cell line (DIP3) was transformed by virally-expressing HPV E7 oncoprotein (DIP3-E7). E7 binds to retinoblastoma protein (Rb) and inactivates it, preventing it from binding to its nuclear targets. Western blotting with anti-Rb antibodies demonstrated that the amount of chromatin-bound Rb was undetectable upon E7 expression and transformation of DIP3. (b) ChIP-PCR showed that in the absence of chromatin-bound Rb, heterochromatic histone modifications H3K9me2, H3K9me3 and H4K20me3 at DXZ1 were decreased. The poised euchromatic mark H3K4me2 was not significantly different at DXZ1 in DIP3 before and after transformation. Enrichment at DXZ1 was calculated as the ratio of immunoprecipitated DNA to input. GAPDH and AFM were used as genic control sites. Error bars represent standard deviations. (c) CENP-A chromatin domain size at DXZ1 was measured using CENP-A immunostaining and FISH in cells over-expressing CENP-A (DIP2-OE) and after HPV-E7-mediated transformation/heterochromatin depletion of a primary fibroblast line DIP3 to create DIP3-E7. Comparisons in CENP-A domain size were made to the parent line (i.e. DIP2 vs DIP2-OE and DIP3 vs DIP3-E7). In each case, CENP-A domain size on DXZ1 increased by 1.5 fold of its original size. Error bars represent standard deviations in the total number of megabases occupied by the CENP-A chromatin domain. (d) CENP-A chromatin domain size on DYZ3 was measured as in (c) in cell lines DIP2-OE and DIP3-E7. Comparisons were made to the parental line in each case (i.e. DIP2 vs DIP2-OE and DIP3 vs DIP3-E7). The domain increased 1.5 times in length over DYZ3 when CENP-A was over-expressed or heterochromatin was depleted from the centromere. Error bars represent standard deviations in the total number of megabases occupied by the CENP-A chromatin domain. Significant differences in (b), (c) and (d) were calculated using a Student’s t-test.