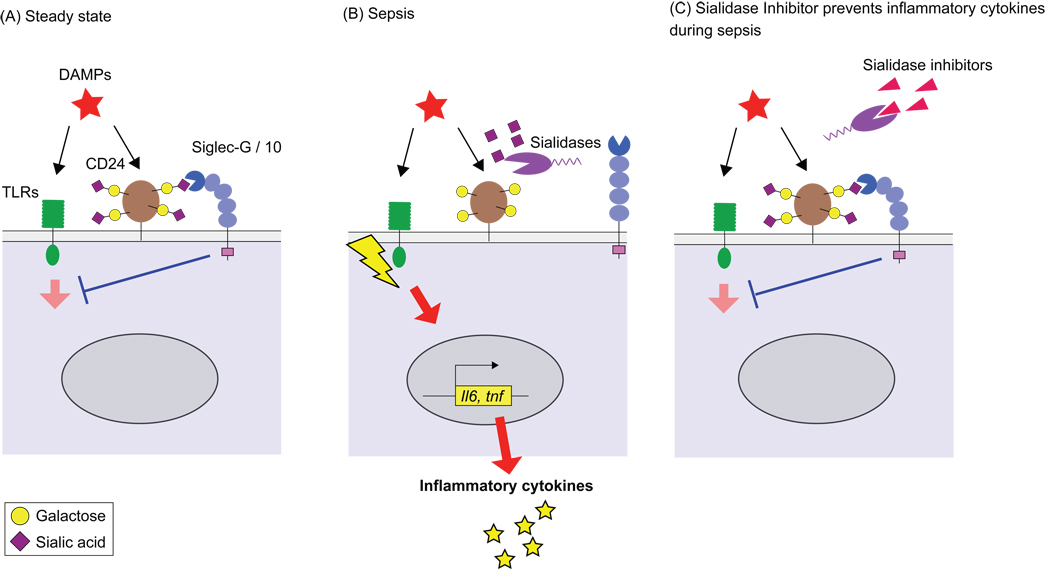
Figure 1.
Sialidase disrupts the Siglec-G inhibitory circuit that suppresses TLR signaling by DAMPs. (A). DAMPs induce a negative inhibition of TLR signaling by binding to a CD24 bound to Siglec-G/10 via recognition of sialic acids on its glycan chains. (B) Bacterial sialidases cleave sialic acids on CD24 disrupting the CD24/Siglec-G/10 inhibitory circuit, leading to enhanced cytokine production. (C) Sialidase inhibitors block the desialylation of CD24, preserving the CD24/Siglec-G/10 inhibitory circuit, and dampening the inflammatory response.