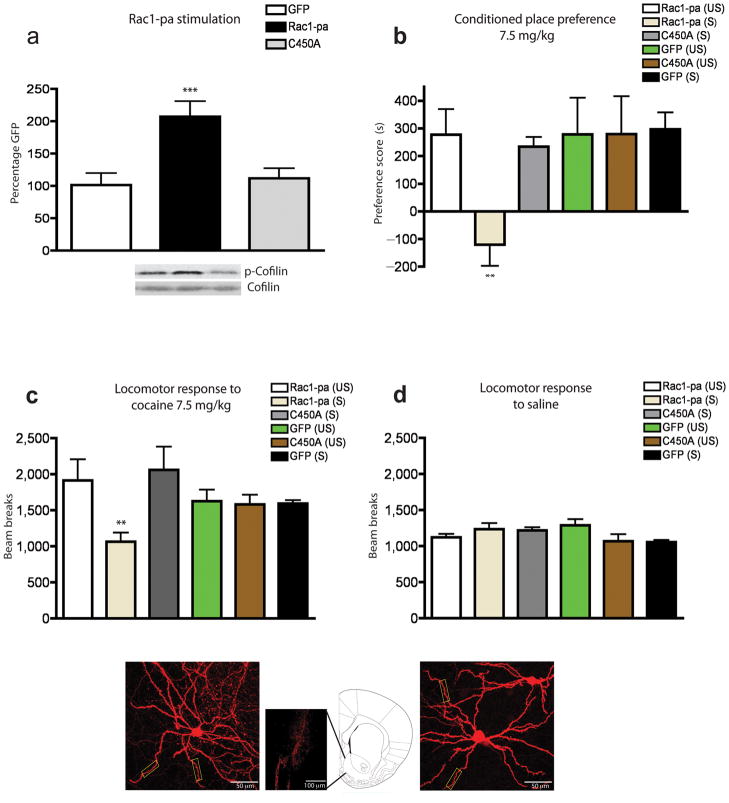
Figure 3. Temporal regulation of Rac1 signaling regulates behavioral responses to cocaine.
(a) Optical stimulation of Rac1 activity (by use of Rac1-pa) increased the phosphorylation state of cofilin (p-cofilin) (F2,13=8.72, ***p<0.005; n=4 mice) while light stimulation of the light insensitive mutant did not alter p-cofilin levels (p>0.05) compared to HSV-GFP controls (n=5 mice per group). Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 3. (b) Such optical stimulation of Rac1 during cocaine pairing [Rac1-pa (S)] also prevented the formation of a conditioned place preference (n=8 mice) (F5,43=2.66, **p<0.01). This blockade required light activation of Rac1, since expression and stimulation of the light insensitive C450A mutant (n=7 mice) or HSV-GFP (n=7 mice) led to the formation of equivalent cocaine preferences as unstimulated (US) control mice (n=8 mice). (c) Light activation of the Rac1-pa construct blocked cocaine-induced increases in locomotion (n=7–8 mice per group) (F4,45=2.43, **p<0.01), (d) but had no effect on locomotor responses to saline (n=7–8 mice per group). (e) A representative infected NAc medium spiny neuron, imaged at 40X, infected with HSV-Rac1-pa. (f) Anatomical placement of viral infection in NAc after HSV injection. (g) A representative infected NAc medium spiny neuron, imaged at 40X, infected with HSV-Rac1-pa-C450A mutant. Rectangular boxes in f and g highlight areas used for dendritic spine analysis. Cartoon shows the location of the injection site at 1.77 mm from Bregma. Data were analyzed by ANOVA and represented as mean ± s.e.m.