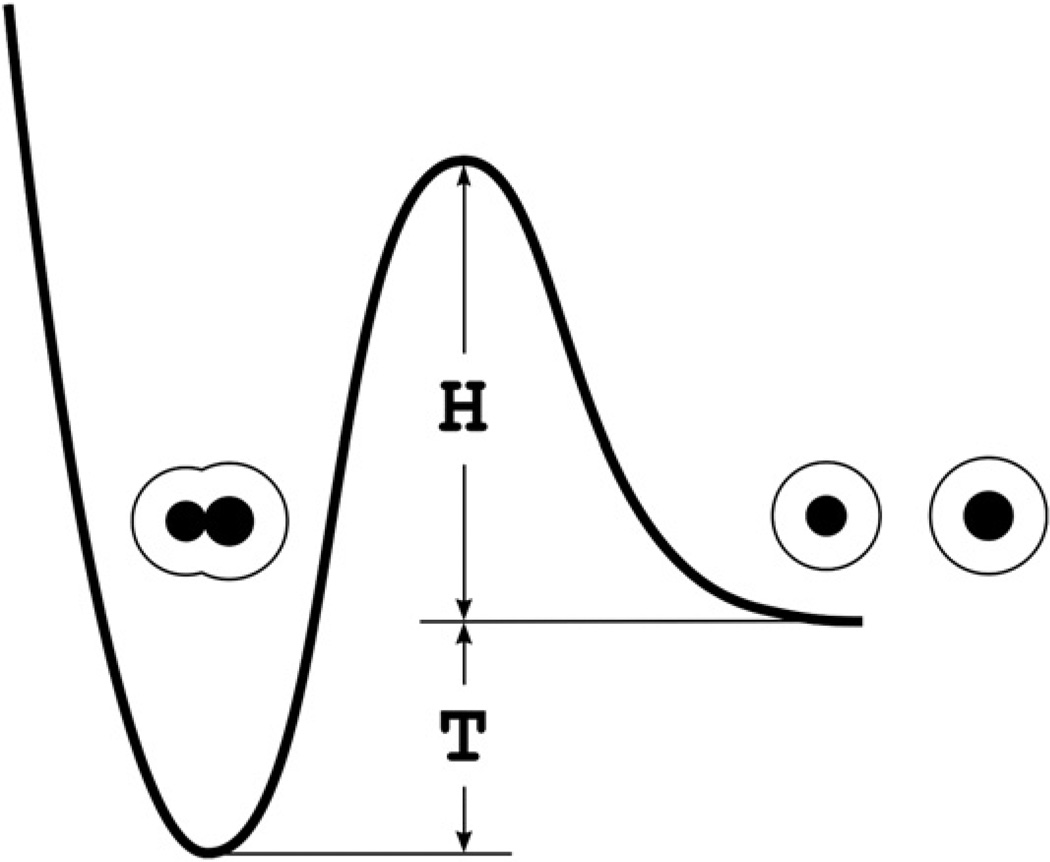
Fig. 3.
An associated complex as the rf-trap. Black spheres are dissolved molecules. The fine lines are the surfaces of their hydration shells. H is the height of the Gw-barrier determining the average rate of the entry into the rf-trap. This height is less than or equal to (3–4) × 20 kJ/mol. T is the thermodynamic stability of the rf-trap. A lifetime of the rf-trap is the average time required to overcome the barrier with the height H + T.