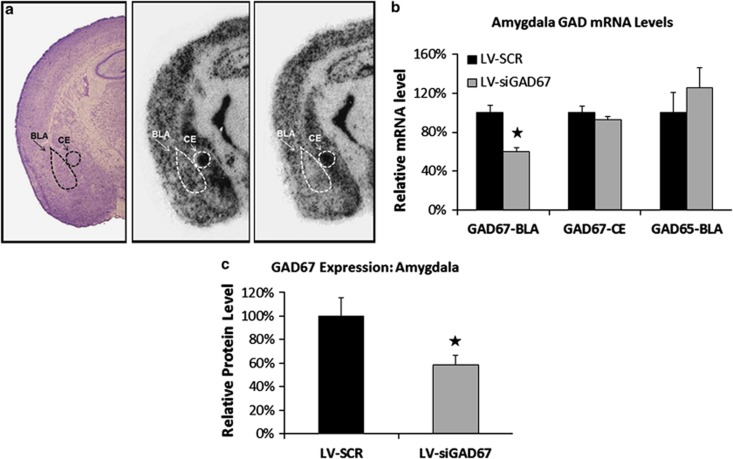
Figure 2.
Reduction in GAD67 mRNA and protein in the amygdala. Levels of protein or mRNA expression were examined in lentiviral (LV)-infected mice 5 days after behavioral testing. In situ hybridization analyses for GAD65 and GAD67 mRNA were conducted on coronal brains sections obtained from half of the experimental animals (n=10 per group). Amygdala brain punches were obtained in remaining half of the experimental animals (n=10 per group) and homogenized samples were subjected to western immunoblot analysis. (a) Qualitative figure showing in situ hybridization of GAD67 mRNA in the basolateral complex of amygdala (BLA) and central nucleus of the amygdala (CEA) following a LV-SCR injection (middle) or LV-siGAD67 injection (right). Also included is a representative Nissl-stained section of LV-infected animal (left). (b, c) LV-siGAD67 mice expressed significantly less GAD67 mRNA and protein when compared with LV-SCR controls. (b) Relative GAD67 mRNA expression (BLA and CEA regions) and GAD65 mRNA expression (BLA only) in LV-SCR and LV-siRNA-infected mice. mRNA levels are expressed as percentages with reference to LV-SCR control animals. (c) Western blot analysis of GAD67 protein levels from amygdala tissue homogenates. Protein amounts determined by western blots were normalized to levels of a GAPDH to loading control and expressed as percentages with reference to LV-SCR control animals. Error bars denote 1 standard error of the mean (s.e.m.). Stars indicated that the difference was statistically significant, P<0.05.