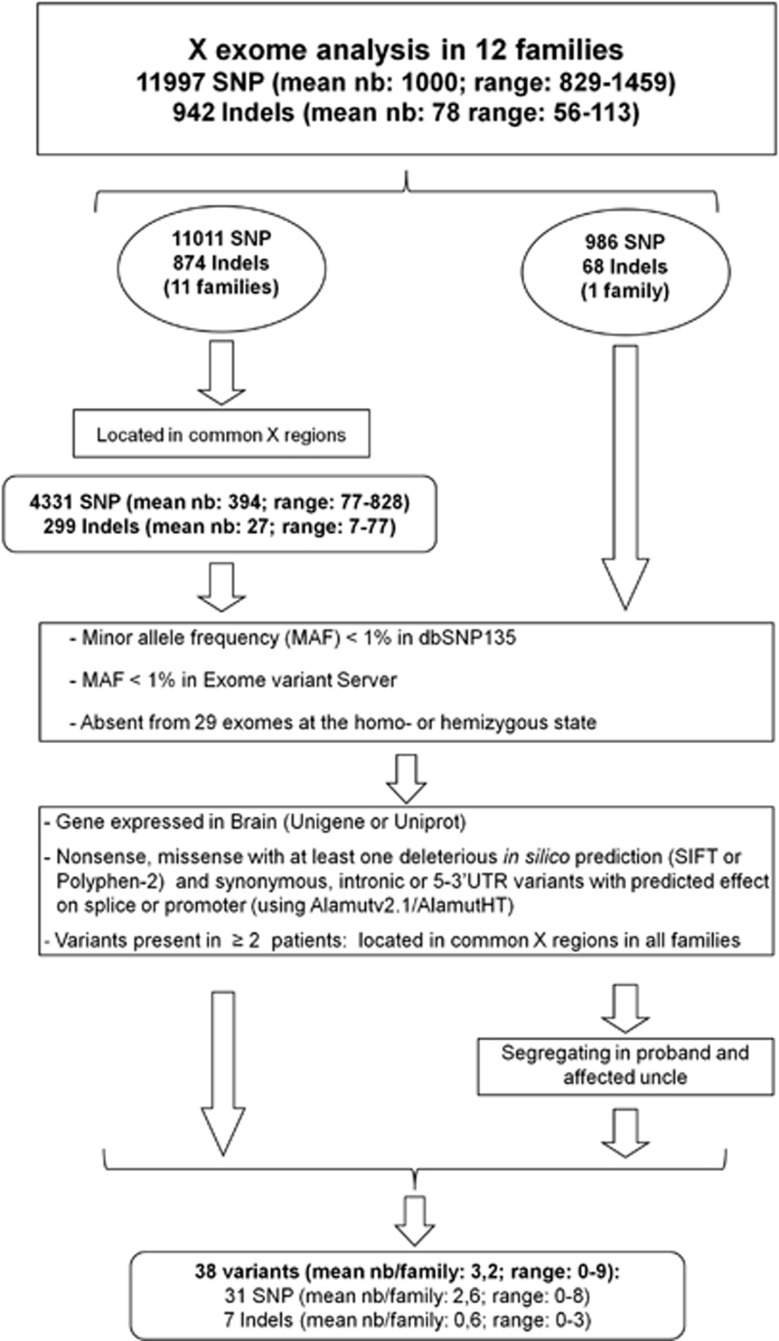
Figure 1.
Strategy used for the selection of rare and possibly deleterious variants. Data from NGS and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays were combined to conserve only variants located in X regions shared by the affected sibs (families 1–11). Further filters included a minor allele frequency (MAF) <1%, expression of the corresponding genes in brain and in silico predictions compatible with an effect of the variant on the gene or the protein (nonsense variants, missense variants with at least one prediction in silico by SIFT (scale-invariant feature transform) or Polyphen-2 that it is deleterious and synonymous, intronic or 5–3′UTR variants with possible effects on splice sites or promoters using Alamutv2.1/AlamutHT). For variants present in at least two index cases, only those that segregated in all affected members of all families were conserved. For one family (family 12), microarray data were unavailable for the affected uncle; segregation of variants found in the index case was performed at a later time.