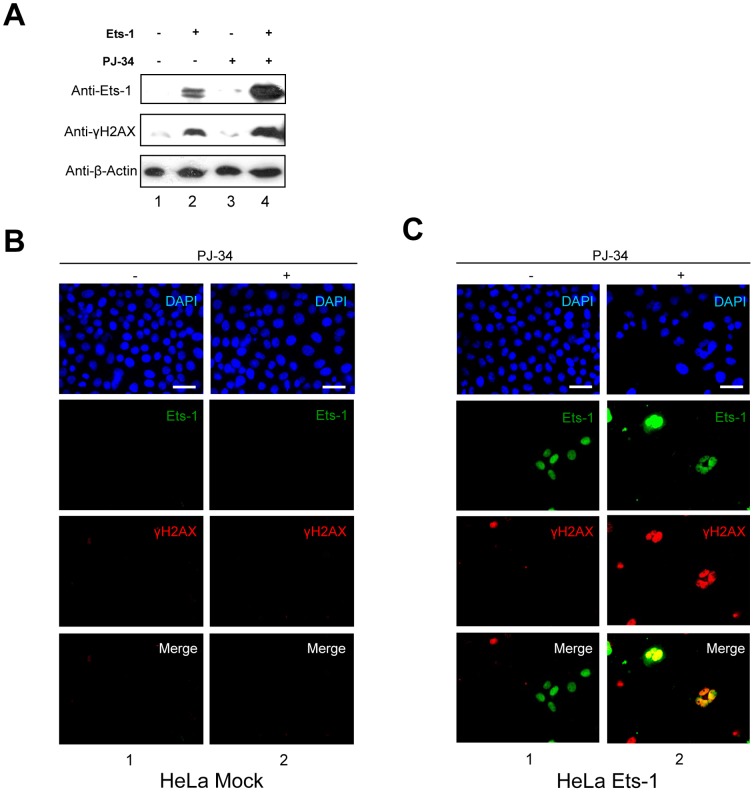
Figure 6. Accumulation of Ets-1 mediated by PARP-1 catalytic inhibition increases DNA damage.
(A) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated H2AX (γH2AX) in transfected HeLa cells treated with PJ-34. pcDNA3 expression vectors without insert (lanes 1 and 3) and encoding Ets-1 (lanes 2 and 4) were transfected in HeLa cells at 50–80% confluence. At 24 h after transfection, cells were treated for 20 h with PJ-34 (10 µM; lanes 3 and 4). Cell lysates (30 µg total proteins) were analysed by Western blot using the C-20 anti-Ets-1 antibody and the anti-γH2AX antibody. (B) Immunofluorescence of γH2AX in HeLa cells treated with PJ-34. HeLa cells were treated with PJ-34 (10 µM) for 20 h. Ets-1 is visualised in green (Alexa Fluor® 488) and γH2AX in red (Alexa Fluor® 594). (C) Immunofluorescence of γH2AX and Ets-1 in transfected HeLa cells treated with PJ-34. HeLa cells were transfected with peGFP-C1-Ets-1 expression vector (1 µg) and treated with PJ-34 for 20 h. γH2AX is visualised in red (Alexa Fluor® 594) and Ets-1 in green (eGFP). In (B) and (C), nuclei were visualised with DAPI staining. Cells were examined by fluorescence microscopy at ×40 magnification. Scale bar = 20 µm.