Figure 2. Association of gender (female) and mortality derived from multivariate-adjusted analyses (n = 7930).
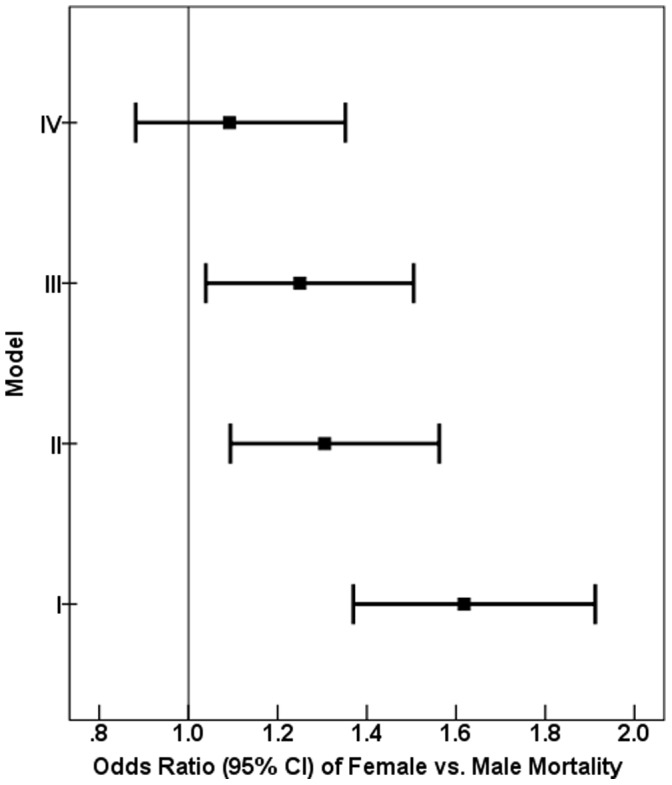
Model I included gender only (n = 6132), (OR = 1.62; 95% CI: 1.37–1.91; P<0.001). Model II was adjusted for gender, age and country (n = 6132), (OR = 1.31; 95% CI: 1.09–1.56; P = 0.003). Model III was adjusted for gender, age, country, diagnosis, Killip class, predominant presenting symptoms, history of CHF and DM (n = 5956), (OR = 1.25; 95% CI: 1.04–1.51; P = 0.018). Smoking, BMI, history of hypertension and hyperlipidaemia were considered but removed because of non-significant associations. Model IV was adjusted for gender, age, country, diagnosis, Killip class, predominant presenting symptoms, history of CHF and DM, discharge medication, including: aspirin, statins, BBs, CCBs, ACE, AIIRBs, and reperfusion (n = 5934), (OR = 1.09; 95% CI: 0.88–1.35; P = 0.417). Smoking, BMI, history of hypertension and hyperlipidaemia, clopidogrel as discharge medication, PCI, and CABG were considered but removed because of non-significant associations. *Predominant presenting symptoms includes: ischemic type chest pain, atypical chest pain, dyspnea, fatigue, loss of consciousness, cardiac arrest/aborted sudden death, palpitation and other symptoms. CI = confidence interval.
