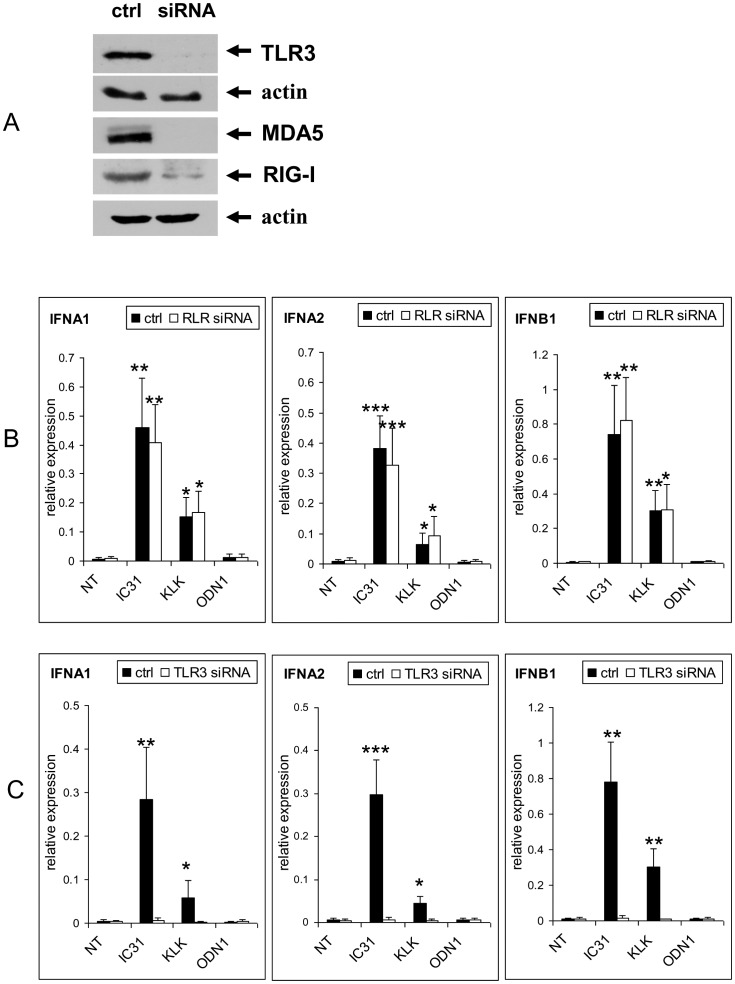
Figure 5. Identification of the receptors and signaling pathways involved in the enhancement of the type I IFN response by IC31®.
Human moDCs were differentiated for 5 days in the absence (NT – “non-treated”) or presence of KLK, ODN1a or IC31® (Protocol B, Figure S2B). In Figures 5B, 5C, 5D and 5E moDCs were activated on day 5 by 20 μg/ml polyI:C for 24 hrs. In Figure 5F DCs were activated by 1 μg/ml CL075 and in Figure 5G by 5 μg/ml CpG2216 (IDC: non-activated immature dendritic cells; MDC: CL075 or CpG2216-activated mature dendritic cells). A – Validation of siRNA activity specific for TLR3 and RLR (RIG-I/MDA5) by Western blotting. B – Comparison of gene expression of type I IFN in control and RLR siRNA treated moDCs. Mean±SEM values of triplicates performed with DCs of two independent donors are shown. C – Comparison of gene expression of type I IFNs in control and TLR3 siRNA treated moDCs. Mean±SEM values of triplicates performed with moDCs of two independent donors are shown. D – Comparison of the levels of secreted IFNβ in control and RLR siRNA treated moDCs. Mean±SEM values of duplicates performed with moDCs of two independent donors are shown. E – Comparison of the levels of secreted IFNβ in control and TLR3 siRNA-treated moDCs. Mean±SEM values of duplicates performed with DCs of two independent donors are shown. F – Effect of TLR7/8 activation by CL075 on IC31®-, KLK- or ODN1a-treated moDCs monitored by IFNβ ELISA. Mean±SEM values of duplicates performed with DCs of two independent donors are shown. G – Effect of TLR9 activation by CpG2216 on IC31®-, KLK- or ODN1a-treated moDCs monitored by IFNβ ELISA. Mean±SEM values of duplicates performed with DCs of two independent donors are shown.