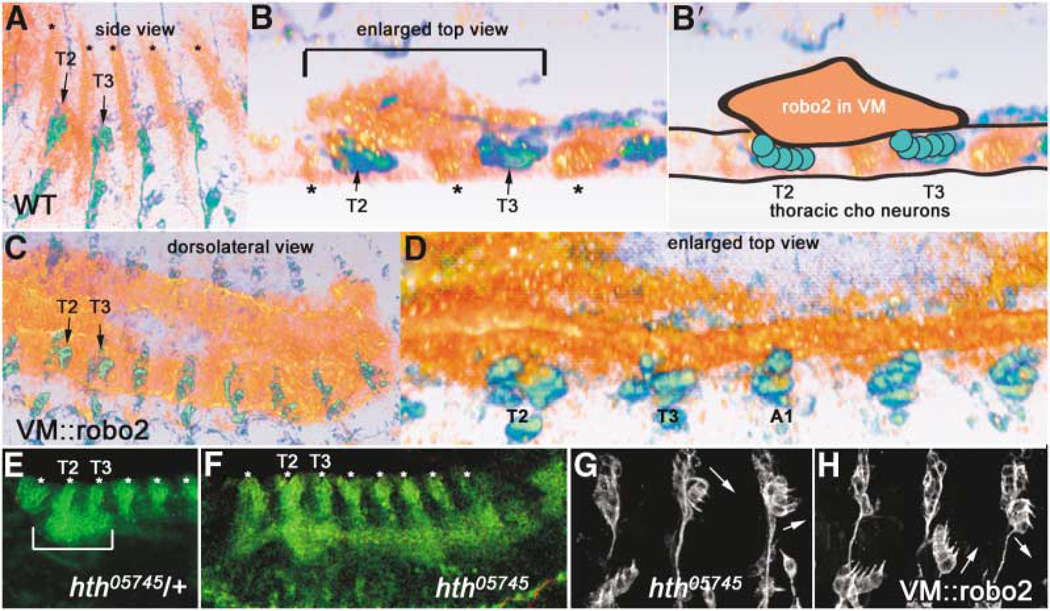
Figure 5. Robo2 Is Expressed in Thoracic Visceral Mesoderm Apposed to Thoracic Chordotonal Neurons, in a Domain Defined by Homeotic Gene Eepression.
(A and B) 22C10 (green/blue) and Robo2 (orange/red) expression in a wild-type stage 14 embryo, shown by volume rendering of a con-focal stack (Amira software). Ectodermal stripes of Robo2 expression are denoted by asterisks.
(A) Side view shows anterior-posterior and dorsoventral extent of Robo2 expression in VM in T2 and T3.
(B) Spatial proximity of the Robo2 VM expression to thoracic Chos can be better visualizedin an enlarged top view (horizontal section)through the same confocal stack, where the thoracic VM Robo2 expression domain is bracketed above the dCh3s in T2 and T3. Interior of the embryo is up. An animated view of the Robo2 expression domains compared to 22C10 can be seen in Movie 3 online.
(B′) Schematic representation of the image in (B), outlining the clump of Robo2 expression in the VM (orange) apposed to thoracic Cho neurons in T2 and T3 (green circles).
(C and D) Ectopic expression of Robo2 with a VM GAL4 driver, showing full posterior extent of robo2 expression at similar stage (C; compare to A) and an enlarged top view (D; compare to B).
(E and F) homothorax mutant embryos at stage 13 (F) have an expanded Robo2 expression domain in the VM (green continuous horizontal stripe that appears to connect the bottoms of the vertical ectodermal Robo2 stripes [asterisks]); compare this pattern to the control (hth/+) embryo (E), whose Robo2 VM expression domain is only in T2 and T3 (bracket).
(H) Driving Robo2 in the abdominal VM transforms Cho organs; the transformed morphologies are identical to those seen when Robo2 is driven in neurons or Cho organs (Figure 2).
(G) A similar phenotype is observed in an hth mutant. Transformations of abdominal lCh5s are noted by arrows. All embryos are oriented with anterior to the left and dorsal up unless otherwise noted. (E) and (F) are slightly ventrolateral views.