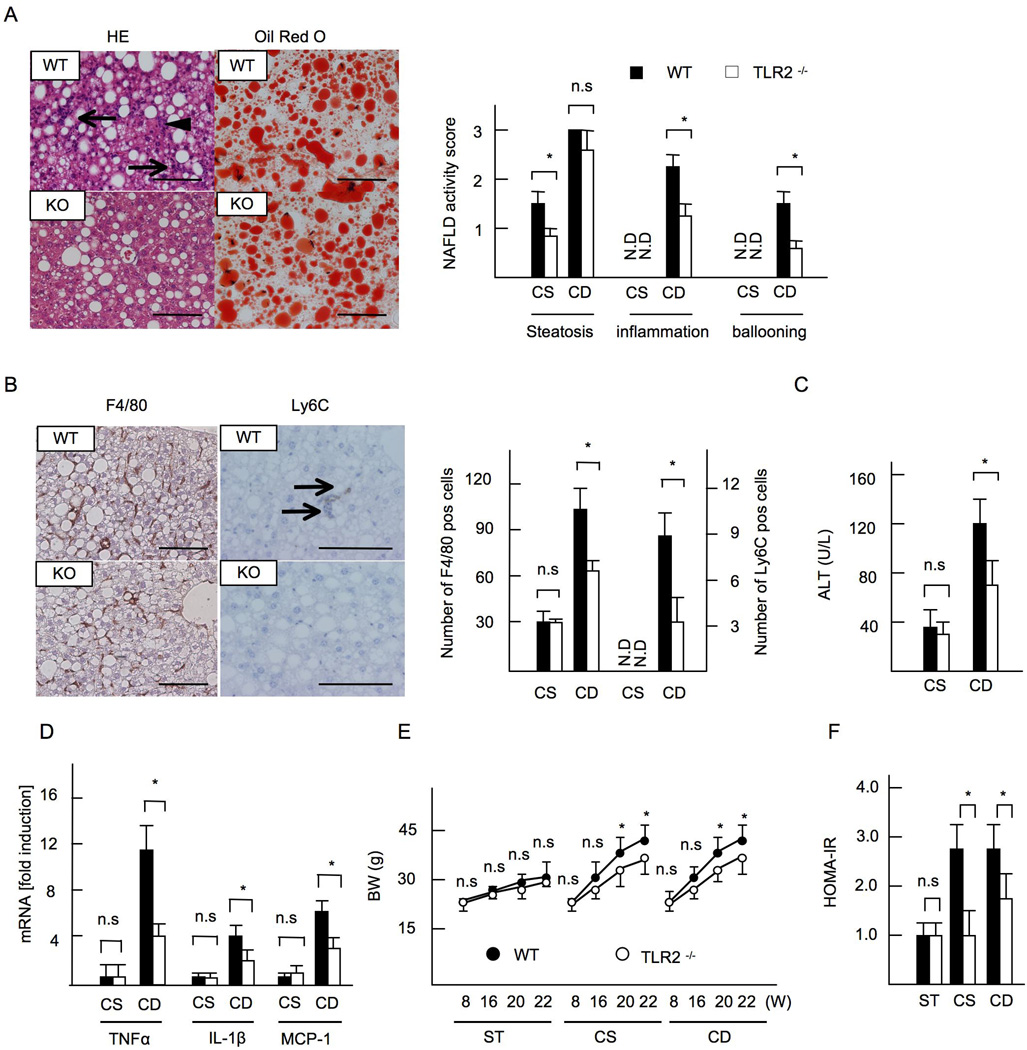
Figure 1. TLR2−/− mice exhibit less inflammation in CDAA-induced NASH.
WT and TLR2−/− mice were fed CSAA diet (CS) or CDAA diet (CD) for 22 weeks. Closed bars indicate WT mice and open bars represent TLR2−/− mice. (A, left) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and oil red O staining. Liver sections on CDAA diet are presented. The grades of steatosis were similar levels in WT and TLR2−/− mice whereas inflammatory cell infiltration (arrows) and hepatocyte ballooning (arrow head) were blunted in TLR2−/− mice. Original magnification,×400 for HE and oil red O staining. Bar 100µm. (A, right) NAFLD activity score. (B) Immunohistochemical staining for F4/80 and Ly6C. Liver sections on CDAA diet are presented. Infiltration of F4/80- and Ly6C-positive cells was suppressed in TLR2−/− mice. Original magnifications,×400 for F4/80,×600 for Ly6C. Bar 100 µm. (B, right) The numbers of F4/80-positive and Ly6C-positve cells. (C) Serum ALT levels. (D) mRNA expression of TNFα, IL-1β, and MCP-1. Genes were normalized to 18S RNA as an internal control. (E, F) Data on mice fed standard chow (ST) were included. (E) Body weight. (F) HOMA-IR. ND; not detected. Data represent mean ±SD, *p<0.05. n.s.; not significant.