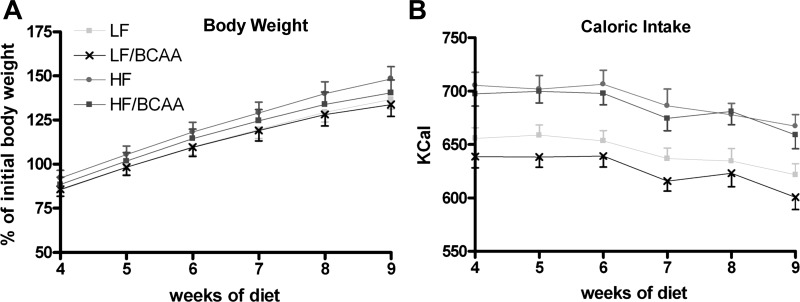
Fig. 1.
The effect of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)-supplemented diets on body weight and food intake. A: body weight was measured weekly throughout the entire 9-wk study. Body weight is presented for weeks 4–9 as %change over control groups (ANOVA: not significant). B: caloric intake was measured weekly throughout the entire 9-wk study. Caloric intake is presented for weeks 4–9 as kcal/week consumed. {ANOVA: diets [low-fat, high-sucrose diet (LF) vs. high-fat diet (HF)], P < 0.0001}. For A and B, n = 15/group. LF/BCAA, low-fat, high-sucrose diet supplemented with leucine, valine, and isoleucine by 150%; HF/BCAA, high-fat diet supplemented with leucine, valine, and isoleucine by 150%.