Fig. 1.
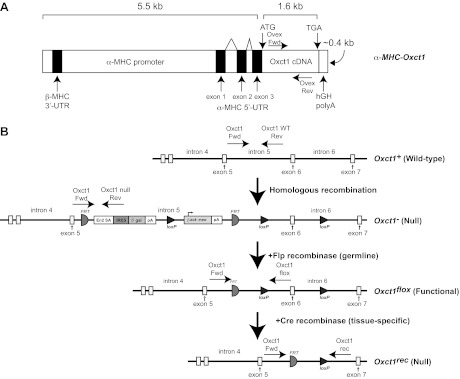
Strategy for the generation of transgenic overexpresser and tissue-specific succinyl-CoA:3-oxoacid CoA transferase (SCOT)-knockout (KO) mice. A: transgenic mice that overexpress coenzyme A (CoA) transferase in cardiomyocytes (SCOT-Heart-OVEX mice). Mouse Oxct1 cDNA was subcloned downstream of the α-myosin heavy chain (MHC) promoter to generate mice overexpressing CoA transferase specifically within cardiomyocytes. ATG, initiator methionine codon; TGA, stop codon; kb, kilobase; UTR, untranslated region. B: schematics depict the endogenous Oxct1 mouse gene (wild type); targeted Null allele (the germline knockout allele); Flox allele, which encodes normal CoA transferase protein; and the recombined Rec (also a null) allele. Polyadenylation (pA) signals in the Null locus terminate transcription after exon 5, and a splice acceptor (SA)/internal ribosomal entry sequence (IRES) results in a truncated and catalytically inactive product from residual message. Flp recombinase recognition target (FRT) sites flank the β-gal and neomycin resistance cassettes and the pA signals. Thus, Flp recombinase mediates removal of the pA transcriptional stop signals and lacZ/neomycin cassette, restoring an active Oxct1 Flox allele in the germline. Exon 6 is flanked by loxP recognition sequences in the Flox allele for cell type-specific Cre recombinase-mediated recombination and inactivation. Genotyping primers for each allele are indicated as horizontal arrows (see Table 1 for sequences). β-gal, β-galactosidase-encoding lacZ gene; β-act:neo, neomycin resistance gene driven by the β-actin promoter.
