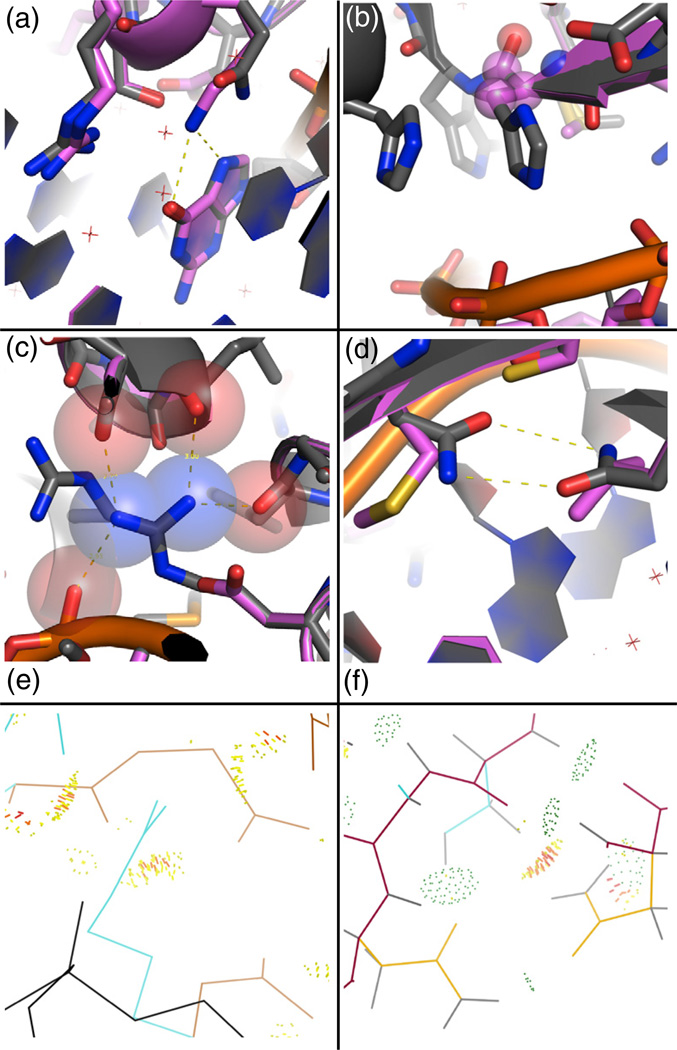
Fig. 9.
Representative failures of the computational methods. Native structure, gray; designed structure, pink. (a) The designed lysine, making a canonical contact with the guanine nucleotide, is calculated to interact more strongly with the DNA than the wild-type glutamine (Gln39, 1zs4), and no interactions with neighboring protein positions are lost from this substitution. (b) A histidine (His97, 2fl3) is redesigned to an alanine, and energetic analysis revealed that the rotamer probability term was mainly responsible for the alanine preference. The High-Temp-Packer method corrects this failure, as the histidine is regained in 71% of the design trajectories, compared to 19% with the DNA-Rebuild method. (c) An arginine residue (Arg432, 1j1v), making multiple contacts to both the protein and DNA backbone atoms, is redesigned to a smaller aspartate residue that makes no favorable interactions. The atoms in the starting crystal structure are very close to each other, and the repulsive clashes cannot be relieved without backbone movement or minimization. (d) A bidentate asparagine–asparagine hydrogen bond is lost (Asn70–Asn90, 2ex5). This failure is also due to repulsive clashes with the nearby protein backbone. (e) Amount of atomic overlap Arg432 in the 1j1v crystal structure calculated using MolProbity.36–38 The atomic overlap is shown with yellow and red dots, DNA is black, side chains are cyan, and the protein backbone is brown. This analysis indicates that the protein backbone and neighboring side-chain residues are clashing with Arg432. Backbone optimization would be required to relieve the clash with the backbone. (f) Atomic overlap (yellow and red dots) between an asparagine residue (yellow) and a hydrogen atom (gray) of the beta-carbon of a neighboring serine residue shown in cyan (2ex5, Asn90–Ser68). Hydrogen bonding between this same serine residue and the other asparagine (Asn70–Ser68) of the bidentate asparagine pair is shown with green dots.