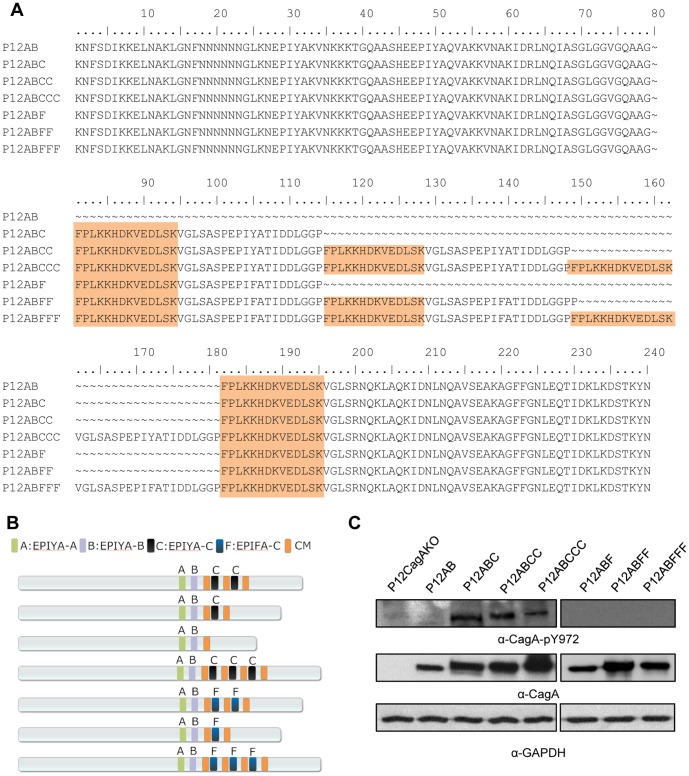
Figure 1. CagA EPIYA-C phosphorylation-functional and -defective H. pylori mutant strains.
(A) Deduced CagA amino acid sequences, following nucleotide sequencing, depicting the EPIYA and EPIFA mutant motifs, as well as the MARK2-kinase inhibitor (CM) (shaded region). (B) Schematic representation of CagA protein expressed by the corresponding mutants. (C) Determination of CagA tyrosine phosphorylation by western blot utilizing α-CagA-pY972 antibody, which recognizes phosphorylated EPIYA-C motifs. CagA and GAPDH expression is also depicted, for control purposes.