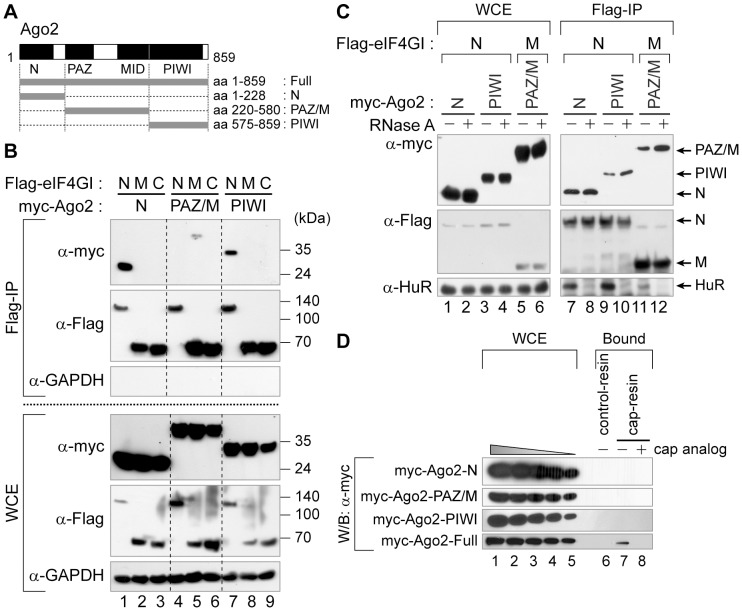
Figure 6. The intact Ago2 associates with the cap-binding complex.
(A) A schematic diagram of human Ago2 and the constructs used for co-immunoprecipitation and cap-pulldown assays. (B) The domains in Ago2 required for the association with eIF4GI. 293FT cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-tagged N-, M- or C-terminal portions of eIF4GI (Figure 5A) together with plasmids expressing myc-tagged Ago2 fragments corresponding to the N, PAZ/M or PIWI domains. Extracts from the transfected cells were incubated with the Flag-resin and the precipitated proteins were visualized by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (C) RNA-independent association of Ago2 domains with eIF4GI domains. RNase-treated (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12) or -untreated (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11) WCE from 293FT cells transiently expressing Flag-tagged eIF4GI derivatives (eIF4GI-N, -M or -C) with myc-tagged Ago2 variants (Ago2-N, -PAZ/M or -PIWI) were subjected to the immunoprecipitation experiments using the Flag-resins. The bound proteins were detected using antibodies indicated. (D) Association of Ago2 domains with the cap-resin. 2 mg of WCEs from 293FT cells transfected with plasmids expressing myc-tagged Ago2 derivatives were applied to cap-pulldown assays and the bound proteins were monitored using anti-myc antibodies. For comparison, various amounts corresponding to 2–0.4% of WCEs used in the pulldown assay were loaded in lanes 1–5.