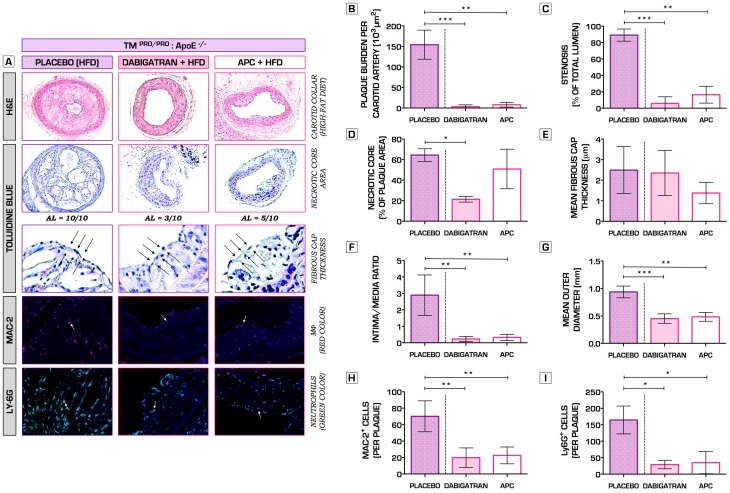
Figure 7. Inhibition of thrombin activity by administration of direct thrombin inhibitor Dabigatran etexilate or recombinant murine APC substantially attenuates leukocyte recruitment and prevents against severe atherosclerosis progression and atherothrombosis.
(A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections of atherosclerotic lesions formed in carotid arteries of TMPro/Pro:ApoE−/− mice, which were assigned to different intervention arms (oral Dabigatran etexilate - 7.5 mg DE/gram chow; i.p. administered bolus doses of recombinant murine APC - 2.5 mg/kg/per every 5 days; or placebo) for a total of 6 weeks after cuff placement around the common carotid arteries (top row). Toluidine blue (TB) stainings were used to quantify the size of necrotic core areas (second and third row). Whereas placebo treated TMPro/Pro:ApoE−/− mice all developed advanced lesions (identified by the presence of necrotic core and fibrous cap formation), Dabigatran etexilate- (3 out of 10, Pearson's chi-squared test (χ 2), n = 10 per group, p = 0.0031 vs. placebo) and rAPC-treated mice (5 out of 10, Pearson's chi-squared test (χ 2), n = 10 per group, p = 0.0325 vs. placebo) had significantly reduced atheromata formed. A total of 5 out 10 animals in the placebo group showed signs of severe plaque vulnerability, whereas none were observed in the intervention arms. Atherosclerotic plaques were further analyzed for the presence of macrophages (MAC-2, red color, fourth row) and neutrophils (Ly-6G, green color, bottom row). Arrows show examples of positive cells. Macrophage and neutrophil infiltration were expressed as the absolute number of Mac-2+ and Ly-6G+ cells per plaque. (B) Administration of either Dabigatran etexilate or rAPC rescued the phenotype and pronouncedly reduced atherosclerotic plaque burden (Placebo: 154.3±35.5*103 µm2; Dabigatran Etexilate: 3.3±4.4*103 µm2, p<0.001; rAPC: 7.9±5.5*103 µm2, p<0.01; n = 10 per group). (C, F, G) These findings were further consolidated by a significant decrease in the degree of stenosis (with ∼80%), intima/media ratio and outward remodeling within the treatment arms of the study (n = 10 per group). (D, E) Except for a significant reduction of the necrotic core area in the Dabigatran etexilate-treated mice as compared to placebo group (n = 10 per group, p<0.05), no other effects were observed with regard to necrotic core formation or fibrous cap thickness. Of note, only mice having advanced lesions were included in these analyses (Dabigatran etexilate: n = 3; rAPC: n = 5). (H, I) In addition, TMPro/Pro:ApoE−/− mice treated with direct thrombin inhibitor or natural anticoagulant rAPC developed an anti-inflammatory stable plaque phenotype, associated with substantially reduced levels of macrophage and neutrophil recruitment. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. Error bars represent mean ± SD. Arrows indicate examples of positive staining/fibrous cap thickness. DNA was counterstained with Hoechst-33342 (blue). Abbreviations: HFD – high-fat diet; AL – advanced atherosclerotic lesion; MФ- macrophage; rAPC – recombinant murine activated protein C.