Figure 4.
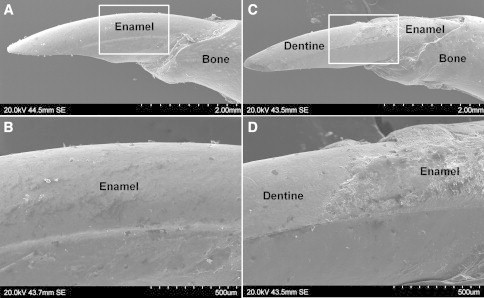
Scanning Electron Microscopy of Mandibular Incisors from Wild-Type and Slc24a4 Knockout Mice
(A) SEM shows the typical mouse incisor morphology of a wild-type mouse where the labial surface of the tooth is completely covered with a smooth layer of enamel. The incisal tip shows the characteristic chisel-like biting edge characteristic of rodents.
(B) Higher magnification of the boxed area in (A) showing the smooth unbroken enamel surface.
(C) SEM of the incisor from a Slc24a4 knockout mouse. Enamel is only present near the cervical margin where the tooth erupts from the mandibular bone. Enamel is missing from the remainder of the tooth (reflecting premature failure) and the underlying dentine surface is exposed. The incisal tip, comprising only softer dentine, is blunted.
(D) Higher magnification of the boxed area in (C) showing the affected enamel to be irregular and poorly mineralized compared to wild-type enamel.
