Figure 1.
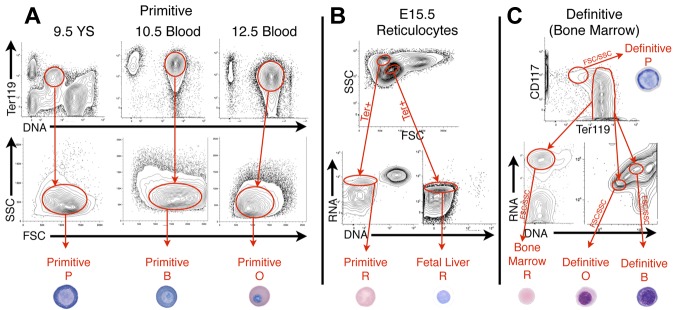
Isolation of primitive and definitive erythroid cells at specific stages of maturation. (A) Because primitive erythroid cells mature semisynchronously, progressive cell stages were isolated from E9.5 yolk sacs (proerythroblasts, P), E10.5 blood (basophilic erythroblasts, B), E12.5 blood (polychromatic/orthochromatic erythroblasts, O), and E15.5 blood (reticulocytes, R, using Ter119 expression, DNA content, and FSC/SSC characteristics. (B) Co-circulating primitive and fetal definitive reticulocytes were isolated from E15.5 blood using FSC/SSC characteristics, Ter119 expression, RNA content (Thiazole Orange, TO), and lack of DNA (VybrantViolet, VV), as described previously.15 (C) Definitive erythroblasts were isolated from BM (shown) and fetal liver (not shown), using Ter119lokit+ for P, Ter119+, VVhigherTOhigher for B, VVlowerTOlower for O, and Ter119+TO+VV− for R. A representative example of each primitive and definitive erythroid cell is shown.
