Figure 3.
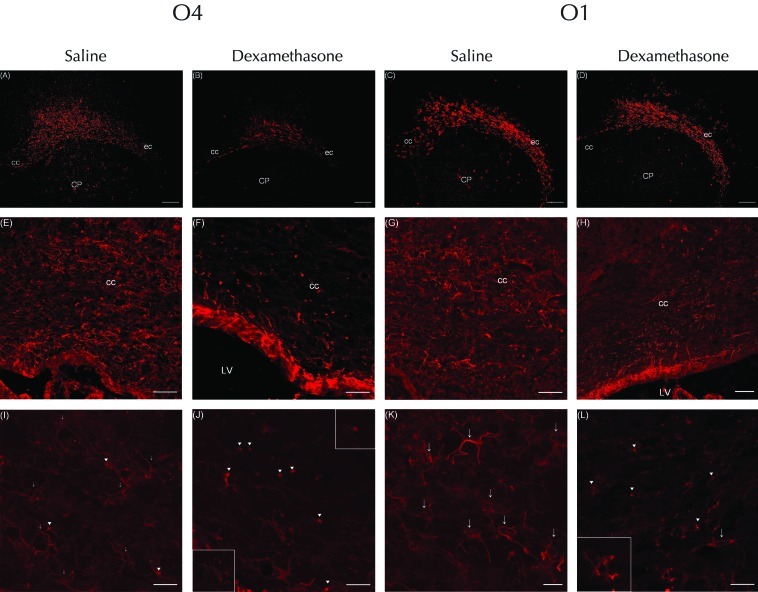
Immunofluorescent staining for (A, B, E, F, I, and J) O4 or (C, D, G, H, K, and L) O1 at P5 in rat pups injected with dexamethasone or saline. The expression of O4-positive cells was decreased in the corpus callosum (cc) and external capsule (ec) of the white matter in the cerebral hemispheres of rats that received (A) dexamethasone compared with (B) saline; (C and D) in contrast, expression of O4 did not differ between groups. At low power, cells labeled with O4 antibody were more numerous in the corpus callosum of rats that received (E) saline compared with (F) dexamethasone. In addition, the corpus callosum of dexamethasone-treated rats showed many pyknotic O4-positive cells with condensation of the cell body. However, at low power, O1-positive cells in the corpus callosum of the (H) dexamethasone group were equivalent in number to those in the (G) saline-treated rats. High-power confocal laser microscopy of (I) O4-positive cells of saline-treated rats revealed simple multipolar cells with several processes. In addition, the corpus callosum contained a few O4-positive cells with condensation of the cell body (arrowheads), but the processes of these were clear, long, and well-branched and -preserved (arrows). In contrast, the (J) pyknotic O4-positive cells of dexamethasone-treated rats displayed features of degeneration, including condensation of the cell body and few processes (arrowheads). The upper-right insert shows the cytoplasmic condensation in more detail; the bottom-left insert highlights the fragmented, tortuous o4-labeled processes. (K) Many O1-positive cells in the saline-treated rats displayed a mature, complex, multipolar morphology characterized by a round soma with clear, long, branched processes (arrows). (L) The corpus callosum of dexamethasone-treated rats contained O1-positive cells that were pyknotic and condensed and had few or bipolar (arrows) processes; the inset shows that these cells had simple multipolar processes and were less mature than those of saline-treated rats. Scale bars, 250 μm (A through D); 100 μm (E through H); and 25 μm (I through L).