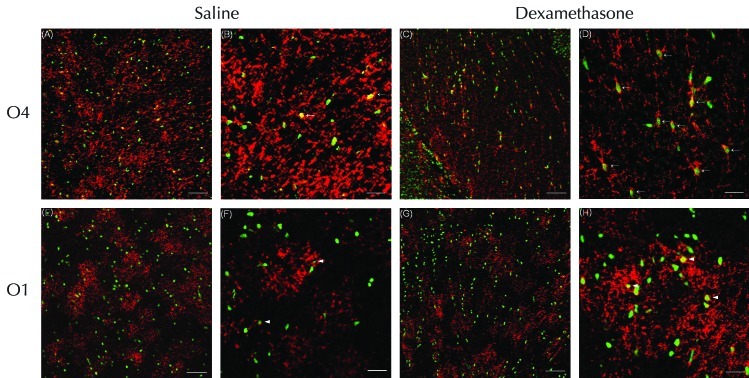
Figure 4.
Confocal laser microscopy of the corpus callosum double-stained on P5 by using TUNEL and O4 or O1 antibody. Numerous TUNEL-positive nuclei (green) were visualized on P5 after administration of (A, B, E, and F) saline or (C, D, G, and H) dexamethasone. The expression of O4-positive cells (red) was increased in the corpus callosum of rats treated with (A) saline compared with (C) dexamethasone. (A through D) O4-positive cells with TUNEL-positive nuclei (suggesting apoptosis) were increased markedly in the corpus callosum of the dexamethasone compared with the saline group. However, administration of dexamethasone did not significantly reduce the expression of (E through H) O1-positive cells overall or those with with TUNEL-positive nuclei in the corpus callosum. High-power microscopy showed that in the corpus callosum, O4-positive cells with TUNEL-positive pyknotic nuclei showed the loss of discrete processes (arrows) in the (D) dexamethosone-treated compared with (B) saline-treated rats, which had a few O4-positive cells with TUNEL-positive nuclei. In contrast, dexamethasone did not alter the processes of O1-positive cells, which were (H) relatively well preserved and similar to those of (F) saline-treated rats. Several O1-positive cells with TUNEL-positive nuclei (arrowheads) were observed in the corpus callosums of both groups. Scale bars, 100 μm (A, C, E, and G) and 25 μm (B, D, F, and H).