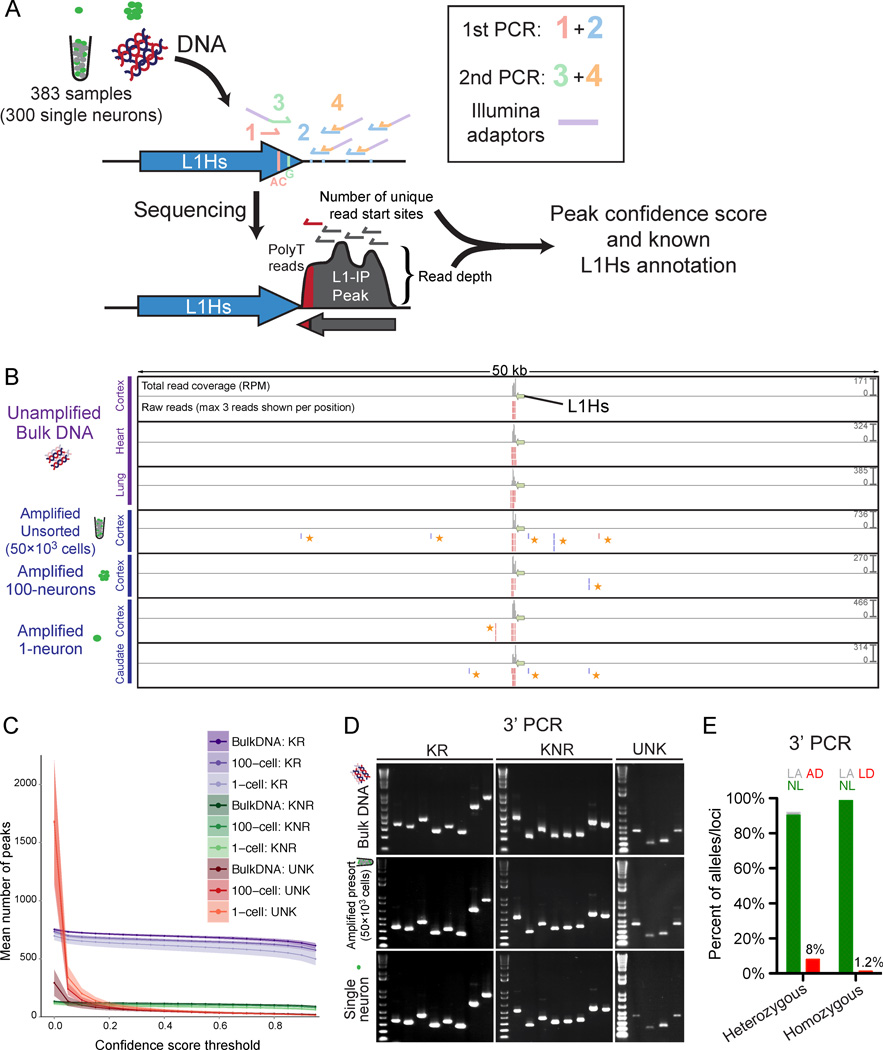
Figure 3. Genome-wide L1Hs insertion profiling (L1-IP) in single neurons.
(A) Schematic of the L1-IP method. Primers 1 and 3 (L1Hs-AC and ILMN-Adaptor1_L1Hs-G, respectively) are specific to L1Hs diagnostic nucleotides. Primer 2 represents 8 different 5bp arbitrary seed primers, each containing the same barcode. Primer 4 (ILMN-SeqAdaptor2) incorporates an Illumina adaptor. See Table S3 for primer sequences.
(B) L1-IP sequencing reads for one representative known reference insertion (L1Hs-KR-chr11_115209613). For each sample, a total read coverage track and a raw reads track are shown. Each read coverage track is scaled to the maximum peak height of the sample (scale on the right, in reads per million mapped reads, RPM). In the raw reads track, up to 3 reads are shown for each position. The green arrow marks the L1Hs insertion. Plus and minus strand reads are red and blue, respectively. Low-level MDA-chimera reads (yellow asterisks) are seen in the local region of the true insertion only in MDA-amplified samples.
(C) The number of peaks found above different confidence score thresholds corresponding to known reference insertions (KR), known non-reference insertions (KNR), and unknown peaks (UNK). Data shown is the mean for all bulk (n=31), 100-cell (n=15) and 1-cell (n=303) samples from all 3 individuals (includes 15, 5 and 3 technical replicates, respectively). Shading around each line shows ±SD. KR and KNR insertions used for peak annotation are in Table S5.
(D) Representative gel images of 3’ junction PCR (3’PCR) of 20 different germline insertions (8 KR, 8 KNR, and 4 UNK).
(E) 3’PCR quantification of AD and LD in 1-neuron samples (n=83), of 3 heterozygous and 3 homozygous L1Hs insertions. AD and LD are quantified for heterozygous and homozygous insertions, respectively. NL, normal amplification; LA, low amplification; AD, allelic-dropout; LD, locus-dropout.
See also Figures S3, S4, S5, and S6.