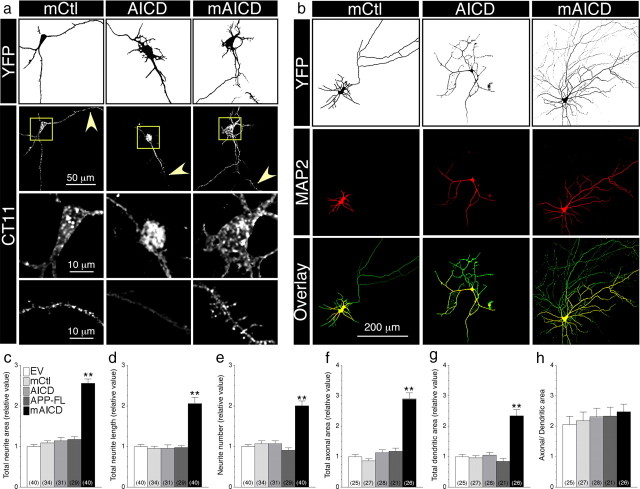
Figure 2.
Membrane-tethered APP intracellular domain promotes exuberant axonal and dendritic arborization in mouse cortical neurons. a, Distribution of mCtl, AICD, and mAICD in primary cortical neurons (8–14 DIV) cotransfected with YFP and the indicated plasmids and immunostained with CT11 antibody. Z-stack images (200 nm interval) were deconvolved and processed for quantification. YFP fluorescence is depicted as inverted images. The bottom two panels represent CT11 staining in enlarged somatic (boxed region) and dendritic areas (indicated by arrowheads). b, Neurons were transfected as above and immunostained with MAP2 antibody. YFP fluorescence is shown as inverted image, and MAP2 staining is shown in red. Overlay images (bottom panel) reveal axons (green) and dendrites (yellow). c–h, Quantitative analysis of neurite outgrowth. Total neurite area (c), total neurite length (d), and neurite number (e) in primary cortical neurons expressing various constructs are plotted relative to YFP/EV-transfected neurons. Total axonal (f) and dendritic areas (g) were also quantified in the same groups of neurons. Differences in axonal and dendritic networks are shown as a change in the ratio between both areas (h). Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's post hoc multiple-comparison analysis. **p < 0.001, compared with neurons transfected with an EV control. The total number of quantified neurons is shown in parentheses. Error bars indicate SEM.