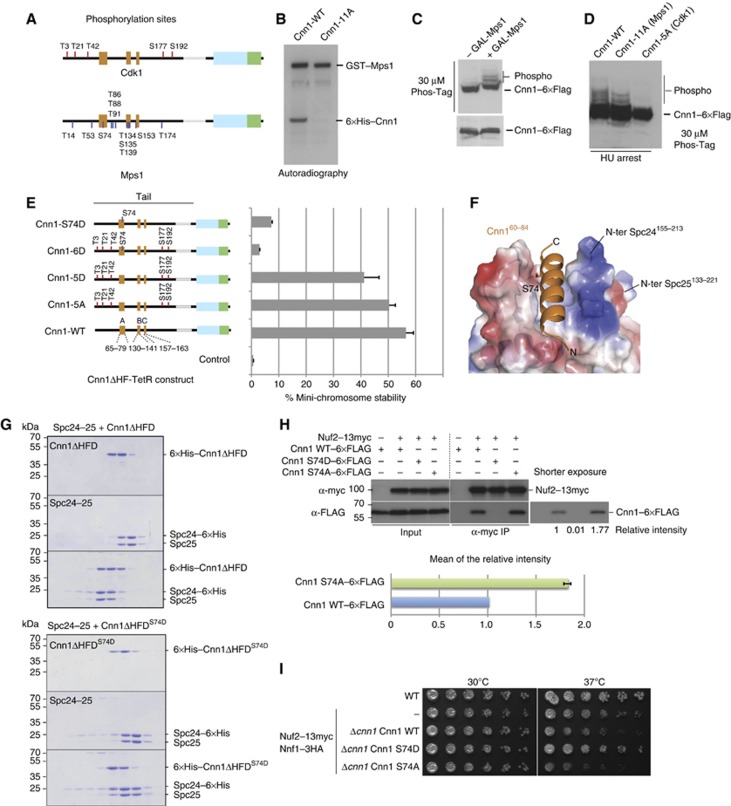
Figure 6.
Phospho-regulation of the Cnn1 N-tail by Cdk1 and Mps1 kinases. (A) Position of Cdk1 and Mps1 phosphorylation sites in Cnn1 as obtained from in vitro phosphorylation and mass spectrometry. See Supplementary Table 3 for a detailed description. (B) Mutation of the mapped Mps1 phosphorylation sites eliminates Mps1-dependent phosphorylation of Cnn1 in vitro. Autoradiography showing kinase reactions with recombinant wild-type and 11A-mutant Cnn1ΔHF phosphorylated by GST-Mps1. (C) Overexpression of Mps1 increases phospho-isoforms of Cnn1 in vivo. Phos-Tag western blot of Cnn1–6 × Flag in the absence or presence of Mps1 overexpression. (D) Alanine mutations of the mapped Cdk1 and Mps1 sites reduce or abolish Cnn1 phospho-isoforms as judged by Phos-Tag western blot. (E) Effects of phospho-eliminating or phospho-mimicking mutations on Cnn1-mediated mini-chromosome segregation. The Cnn1 construct is indicated in the left panel, the corresponding plasmid stability on the right. Error bars denote s.e.m. n=3. (F) Location of Ser74 in the Spc24-25–Cnn1 structure. Note that Ser74 is located in the Cnn1 binding pocket. Electrostatic potential coding: blue, −71 kT/e; red, +71 kT/e. (G) Coomassie-stained gels of analytical size-exclusion chromatography performed with 12 μM Spc24-25, 12 μM Cnn1ΔHFD, and their combination (above); 12 μM Spc24-25, 12 μM Cnn1ΔHFDS74D, and their combination (below). The abolished complex formation caused by S74D mutation is indicated by the lack of a shift to earlier elution volumes of both molecules. (H) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments from log-phase cell extracts visualizing the interaction between Cnn1–6 × Flag wild-type and S74D or S74A mutants with Nuf2–13 × myc (Ndc80 complex). The intensity of the bands relative to the wild-type Cnn1 is reported below the western blot and quantified for the S74A mutant compared to the wild type in the lower panel. Error bar denotes s.e.m. (n=3). (I) Spot assays performed by plating four-fold dilutions of the indicated strains at different temperatures on YPD plates.