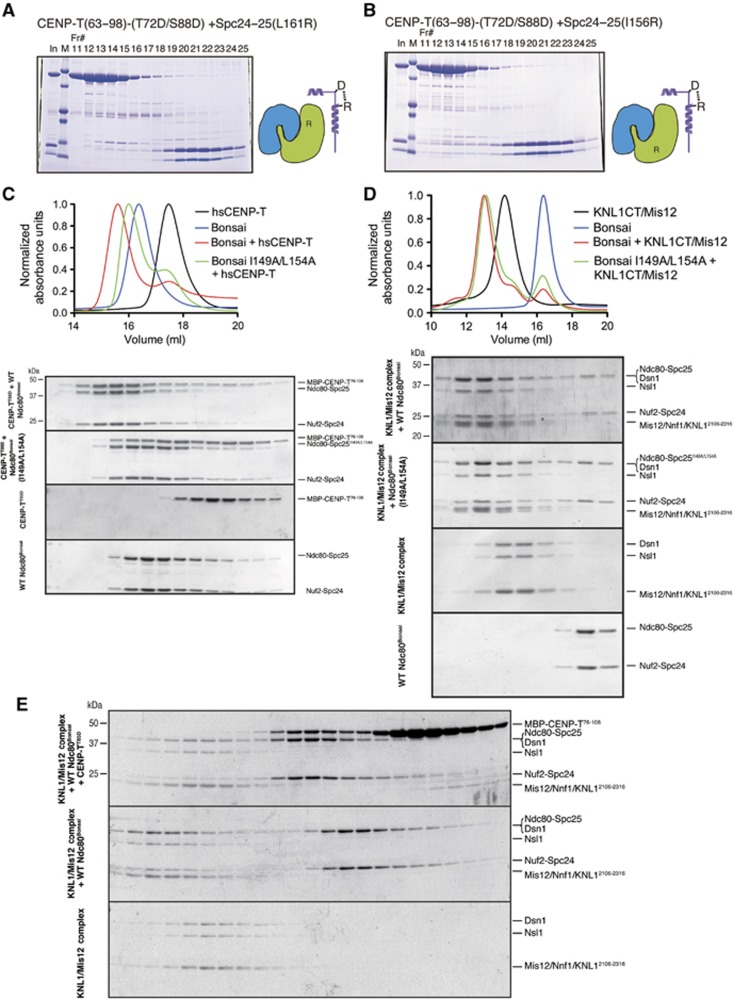
Figure 5.
Binding of CENP-T and the Mis12 complex to the Ndc80 complex is mutually exclusive. (A) L161R mutations in Spc25 disrupt the interaction with CENP-T. Phospho-mimetic chicken MBP-CENP-T63–98 (T72D/S88D) and the mutant Spc24125–195/Spc25132–234 (L161R) complex were separated by gel filtration using a Superdex 75, analysed by SDS–PAGE, and stained with Coomassie. (B) I156R mutations in Spc25 disrupt the interaction with CENP-T. Phospho-mimetic MBP-CENP-T63–98 (T72D/S88D) and the mutant Spc24125–195/Spc25132–234 (I156R) complex were analysed by gel filtration as in (A). (C) I149A L154A double mutants in human Spc25 disrupt binding to human CENP-T. Human phospho-mimetic CENP-T (MBP-hsCENP-T76–106 T85D) and the wild-type Ndc80Bonsai complex or the Ndc80Bonsai I149A L154A mutant complex were mixed and analysed by gel filtration. Protein mixtures were incubated on ice for 30 min before conducting the chromatography using a Superose 6 column. Fractions were collected, analysed by SDS–PAGE, and stained with Coomassie. Elution profiles from the size-exclusion chromatography for the experiment are shown (top). Elution of proteins was monitored at A280 nm. (D) The Ndc80Bonsai complex or the Ndc80Bonsai I149A L154A mutant complex and the human Mis12–KNL12106–2316 complex were mixed and analysed by gel filtration chromatography using a Superose 6 column as in (C). Elution profiles from the size-exclusion chromatography are shown (top). (E) CENP-T and the Mis12/KNL1CT complex show mutually exclusive binding to the Ndc80Bonsai complex. Human phospho-mimetic MBP-CENP-T76–106(T85D), wild-type Ndc80Bonsai complex, and the human Mis12-KNL12106–2316 complex were mixed in the indicated combinations and analysed by gel filtration. A large complex containing all components was not detected, although both CENP-T and KNL1/Mis12 bound individually to the Ndc80 complex based on altered migration.