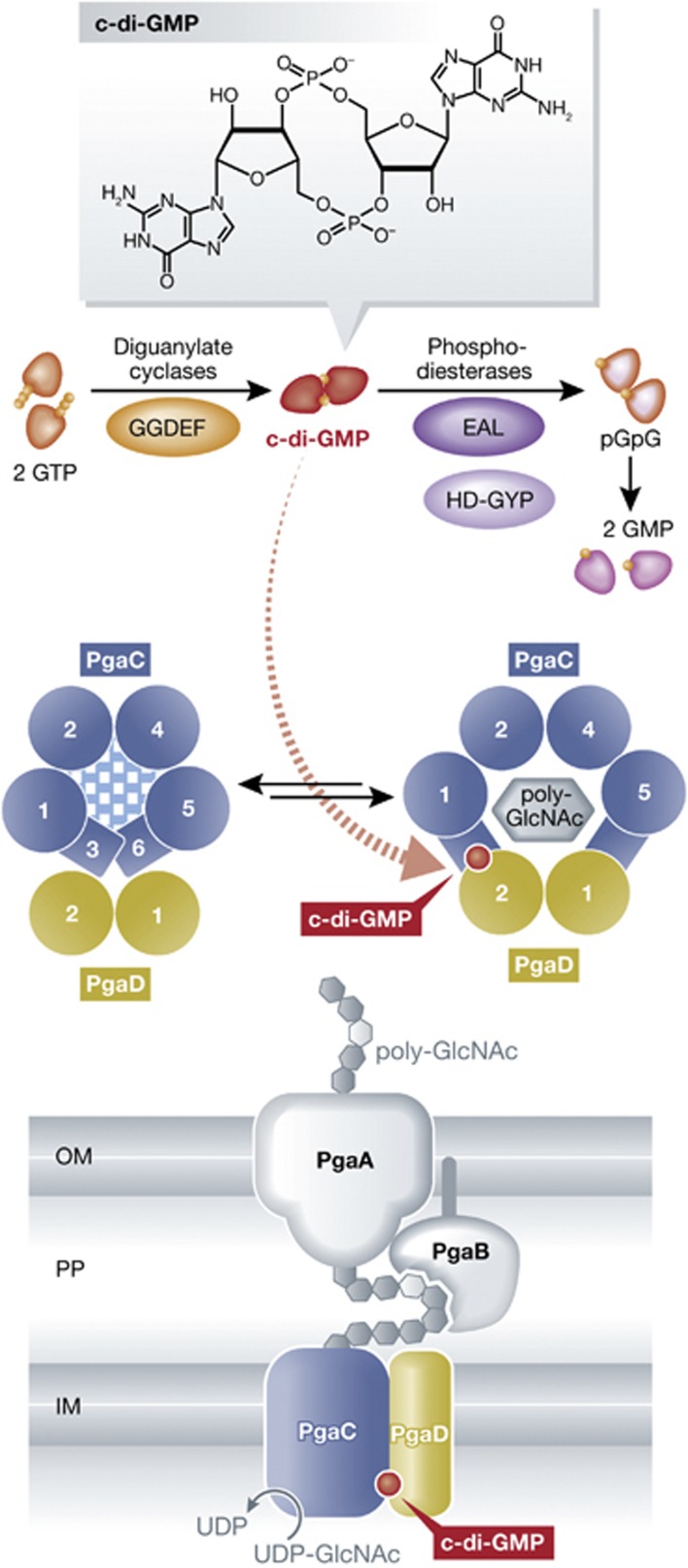
Figure 1.
C-di-GMP accumulation promotes complex formation of PgaC and PgaD resulting in synthesis and secretion of the biofilm matrix exopolysaccharide poly-GlcNAc (PGA). Among the diguanylate cyclases (which carry GGDEF domains) in E. coli, mainly YdeH is involved in generating c-di-GMP that binds simultanously to the membrane-inserted proteins PgaC and PgaD. C-di-GMP binding stabilizes the PgaCD complex, activates its glycosyltransferase activity and allows secretion of the product PGA. Without c-di-GMP bound, PgaD is subject to proteolysis. Circles with numbers symbolize the transmembrane alpha helices of PgaC and PgaD as seen perpendicular to the plane of the cytoplasmic membrane. For further details, see text.