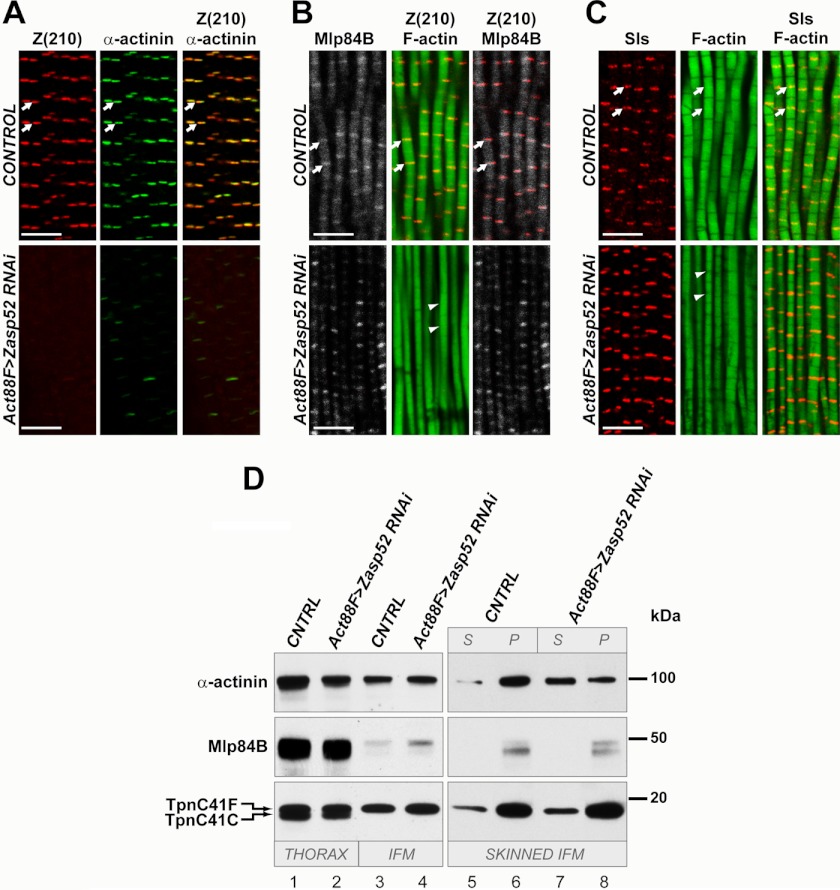
FIGURE 5.
Zasp52 is required for proper myofibril organization in adult flies. A, immunostaining of horizontal frozen sections of thoraces from control flies (upper panels) and from Zasp52KD flies (lower panels), using anti-Z(210) (left panels) or anti-α-actinin (middle panels) antibodies. Right panels represent merged anti-Z(210) and anti-α-actinin images. For control, y w were crossed with Act88F-gal4 flies, and offspring were assayed. Note the failure of α-actinin to accumulate at the Z-disks in the knockdown animals. B, immunostaining of frozen sections of control flies (upper panels) and Zasp52KD flies (lower panels), using anti-Z(210), anti-Mlp84B, and phalloidin. For control, y w were crossed with Act88F-gal4, and their offspring were assayed. The middle and right panels represent merged anti-Z(210) and phalloidin, or merged anti-Z(210) and anti-Mlp84B images, respectively. Note that Mlp84B accumulation remains normal in the Zasp52 knockdown muscles. C, immunostaining of frozen sections from control (upper panels) and Zasp52KD (lower panels) adult thoraces, using anti-Sls antibody and phalloidin. For control, y w were crossed with Act88F-gal4 flies, and the offspring were assayed. Note that Sls accumulation and localization is normal in Zasp52 knockdown muscles. A–C: white arrows point to Z-lines. White arrowheads show absence of distinct Z-lines on phalloidin images of Zasp52KD flies. Scale bars 5 μm. D, Western blot of proteins from control or Zasp52KD flies. Proteins from whole thoraces (lanes 1, 2), dissected flight muscles only (lanes 3, 4), or skinned flight muscles (lanes 5–8) were reacted with anti-α-actinin or anti-Mlp84B antibodies. Anti-troponin C (TpnC) staining was used as a protein-loading control. This antibody recognizes two different adult TpnC isoforms, with TpnC41F being expressed in the flight muscles. For control (CNTRL), y w were crossed with Act88F-gal4, and adult offspring were assayed. Note that despite the loss of α-actinin from the Z-discs, apparently normal levels of α-actinin are detected in Zasp52KD muscles. Note that flight muscle levels of Mlp84B are significantly lower than those in whole thoraces. Skinned IFM, lanes 5–8: muscle samples were treated as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Aliquots of supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions from the first centrifugation step were analyzed to determine the subcellular locations of the proteins under investigation. Note that Mlp84B and TpnC are predominantly in the pellet (i.e. myofibril fraction) in CNTRL and KD animals. By contrast, α-actinin is present in the pellet in CNTRL animals, but strongly enriched in the supernatant in KD samples.