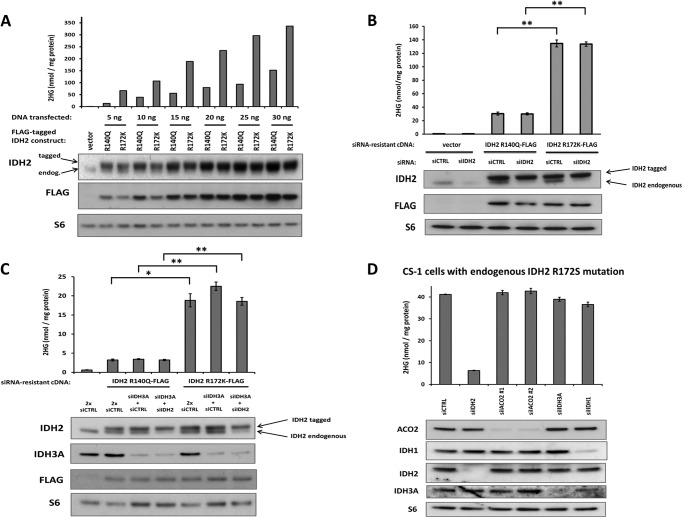
FIGURE 1.
Mitochondrial IDH2 Arg-140 mutations result in less cellular 2HG accumulation than IDH2 Arg-172 mutations, and 2HG accumulation from both mutations is insensitive to depletion of wild-type IDH. A, FLAG-tagged IDH2 R140Q and R172K cDNA constructs, or empty vector, were transfected into 293T cells at various doses. Cells were harvested 48 h post-transfection and assessed for 2HG accumulation by GC-MS (top) or protein expression by Western blot (bottom). Data are from a representative of 3 independent experiments. B, FLAG-tagged IDH2 R140Q and R172K constructs engineered to be resistant to siRNA knockdown, or empty vector, were transfected into cells along with 50 pmol of non-targeting siRNA (siCTRL) or 50 pmol of siRNA targeting only the endogenous wild-type IDH2 (siIDH2). C, siRNA-resistant IDH2 constructs were transfected into cells along with 60 pmol of siCTRL (2x siCTRL), 30 pmol of siRNA targeting the α subunit of IDH3 (siIDH3A) plus 30 pmol of siCTRL, or 30 pmol of siIDH3A plus 30 pmol of siIDH2. D, CS-1 chondrosarcoma cells with a naturally occurring, endogenous, monoallelic IDH2 R172S mutation were transfected with 30 pmol of siCTRL, siIDH2 (targeting both wild-type and mutant IDH2), one of two independent siRNAs targeting the mitochondrial aconitase ACO2 (siACO2#1 and #2), siIDH3A, or siIDH1. For B-D, data are representative of mean ± S.D. of 3 biological replicates from 2 independent experiments. *, p < 0.005; **, p < 0.001.