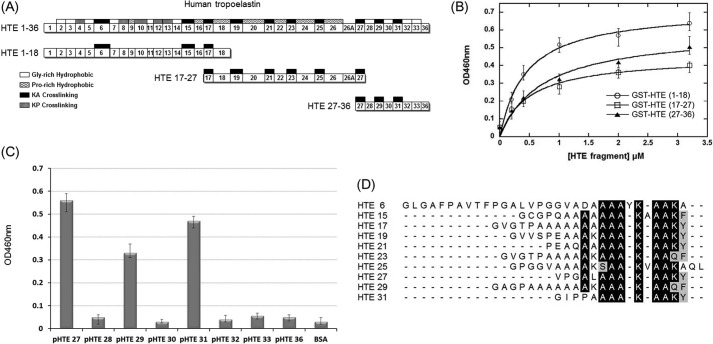
FIGURE 2.
Mapping the binding fragments of MTB Ag85B on HTE. A, schematic diagram showing the HTE and truncated HTE fragments (including HTE(1–18), HTE(17–27), and HTE(27–36)) used in this study. All repeating module types are indicated on the full-length HTE, although only KA-cross-linking domains are shown on the truncated HTE fragments. B, binding of truncated M. tuberculosis Ag85B to immobilized recombinant GST-tagged truncated HTE fragments. Various concentrations (0, 0.2, 0.4, 1, 2, and 3.2 μm) of truncated HTE fragments were coated on microtiter plate wells, incubated with His-tagged M. tuberculosis Ag85B (0.2 μm), and detected by ELISA. The measured KD values were 0.44 ± 0.08 μm (HTE(1–18)) and 0.49 ± 0.15 μm (HTE (17–27)), and 0.53 ± 0.18 μm (HTE (27–36)). Each value represents the mean ± S.D. of three trials performed in triplicate samples. C, eight synthetic peptides (2 μm) based on the sequence of HTE(27–36) fragments were immobilized on microtiter plate wells, incubated with His-tagged M. tuberculosis Ag85B (0.2 μm), and detected by ELISA. D, sequence alignment of the M. tuberculosis Ag85B-binding peptides and other HTE KA-cross-linking domains reveals a conserved motif, AAAKAAKY. The conserved residues are highlighted (identical is black; and similar is gray).