FIGURE 5.
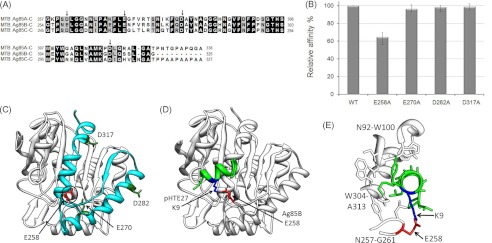
Identification of the key positively charged residues of MTB Ag85 involved in HTE binding. A, sequence alignment of the C termini of M. tuberculosis Ag85, subtypes Ag85A, Ag85B, and Ag85C. The arrows indicated the conserved negatively charged residues. B, four His-tagged mutants (E258A, E270A, D282A, and D317A) derived from M. tuberculosis Ag85B were added to microtiter plate wells coated with 1 μg of recombinant GST-tagged HTE. Bound proteins were detected by ELISA. Wild-type M. tuberculosis Ag85B (WT) served as a positive control. C, structure of M. tuberculosis Ag85B (Protein Data Bank code 1f0n) (36) was used to depict the M. tuberculosis Ag85B-C (residues 254–325) (cyan) region and the conserved negatively charged residues in this region. The HTE-interacting residue, Glu-258, is shown in red. D, Ag85B-pHTE 27 docking model. ClusPro 2.0 (34) was used to dock pHTE 27 (green) (35) onto the Ag85B structure (white) (36). The lowest energy structure after refinement with FireDock (37) includes the proposed electrostatic interaction. E, detailed view of the Ag85B-pHTE 27-binding site. pHTE 27 is positioned within a groove on the Ag85B surface.
