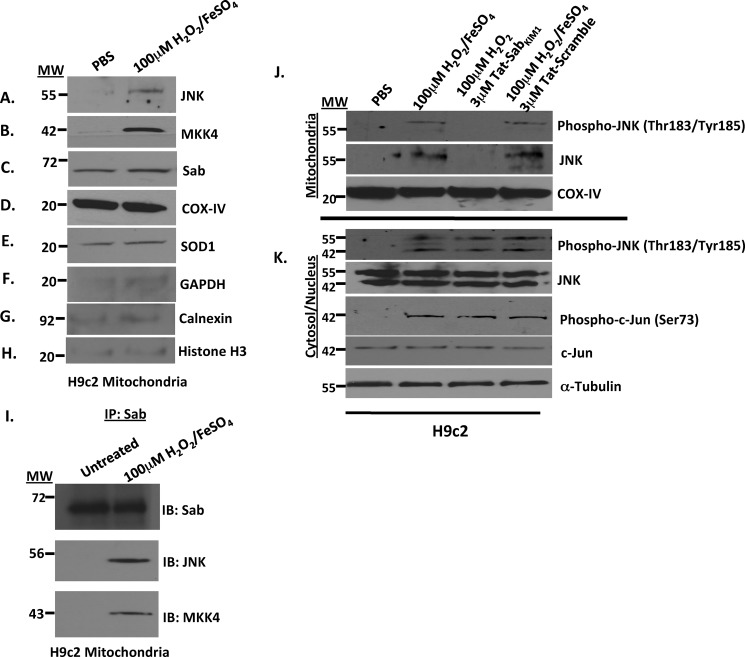
FIGURE 2.
Oxidative stress induced by H2O2/FeSO4 caused JNK and MKK4 translocation to the mitochondria in rat H9c2 cardiomyocyte-like cells. A–H, mitochondria isolations were prepared from rat H9c2 cardiomyocyte-like cells stressed with 100 μm H2O2/FeSO4 for 20 min. The mitochondria were then monitored for JNK, MKK4, Sab, COX-IV, SOD1, and GAPDH by Western analysis. COX-IV and SOD1 served as the mitochondria loading controls, and GAPDH, calnexin, and histone H3 served as controls for cytosolic, microsomal, and nuclear contamination, respectively. I, JNK interacts with Sab and MKK4 on the mitochondria in rat H9c2 cardiomyocyte-like cells. The mitochondrial complex was isolated from rat H9c2 cardiomyocyte-like cells stressed with 100 μm H2O2/FeSO4 for 20 min, immunoprecipitated with Sab antibody, and then immunoblotted for Sab, JNK, and MKK4. J, disruption of the JNK-Sab interaction by Tat-SabKIM1 peptide prevented JNK localization on the mitochondria. Mitochondria isolations were prepared from rat H9c2 cardiomyocyte-like cells stressed with 100 μm H2O2/FeSO4 for 20 min and probed for phospho-JNK and JNK in the presence and absence of 3 μm Tat-SabKIM1 or Tat-scramble peptide. COX-IV served as the mitochondrial loading control. K, cytosol/nuclear isolations from rat H9c2 cardiomyocyte-like cells stressed with 100 μm H2O2/FeSO4 for 20 min and probed for phospho-JNK, JNK, phospho-c-Jun, and c-Jun in the presence and absence of 3 μm Tat-Sab or Tat-scramble peptide. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control.