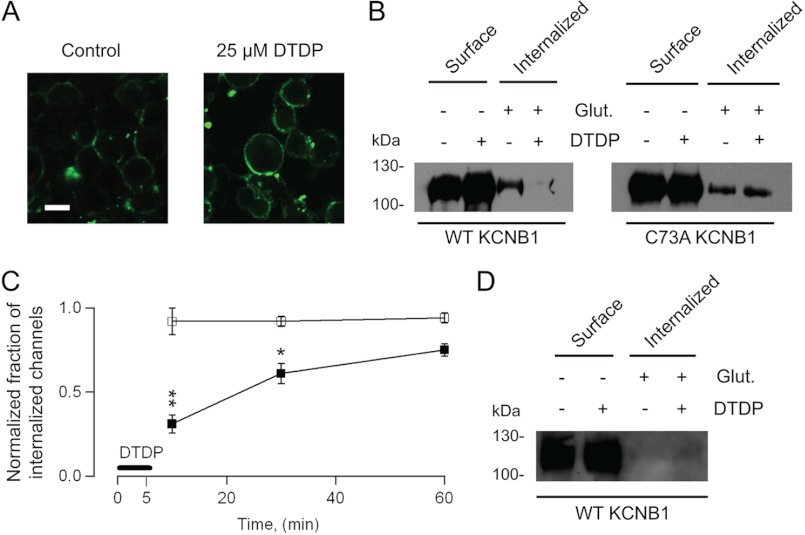
FIGURE 1.
Oxidized KCNB1 channels exhibit defective internalization. A, representative confocal images of N2A cells transfected with wild-type KCNB1-HA in control cells or after 5-min incubation with 25 μm dTDP. Proteins were labeled with biotin and with a streptavidin-FITC-conjugated secondary antibody. Scale bar = 5 μm. B, − glutathione (Glut.) lanes: representative Western blot analysis visualization of wild-type and C73A KCNB1-HA channels in the plasma membrane of N2A cells in control cells or subjected to an oxidative insult. + glutathione lanes, fraction of internalized wild-type and C73A KCNB1-HA channels in a 10-min interval. Channels were labeled with impermeant biotin derivative sulfo-NHS-SS-biotin and incubated for 5 min in DMEM containing 25 μm dTDP and for an additional 5 min in normal DMEM. Then the cells were either washed with PBS (− glutathione) or 75 mm reduced glutathione in PBS (+ glutathione) to remove surface biotin, immunoprecipitated with streptavidin-agarose beads, and immunoblotted with monoclonal anti-HA antibody. C, fraction of internalized wild-type or C73A channels 10, 30, and 60 min after an oxidative insult (DTDP) normalized to the fraction of internalized channels in the control. Densitometry analysis was performed using ImageJ 1.44 software (National Institutes of Health). n = 3–5 experiments/point. D, as in B in cells maintained at 4 °C. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.