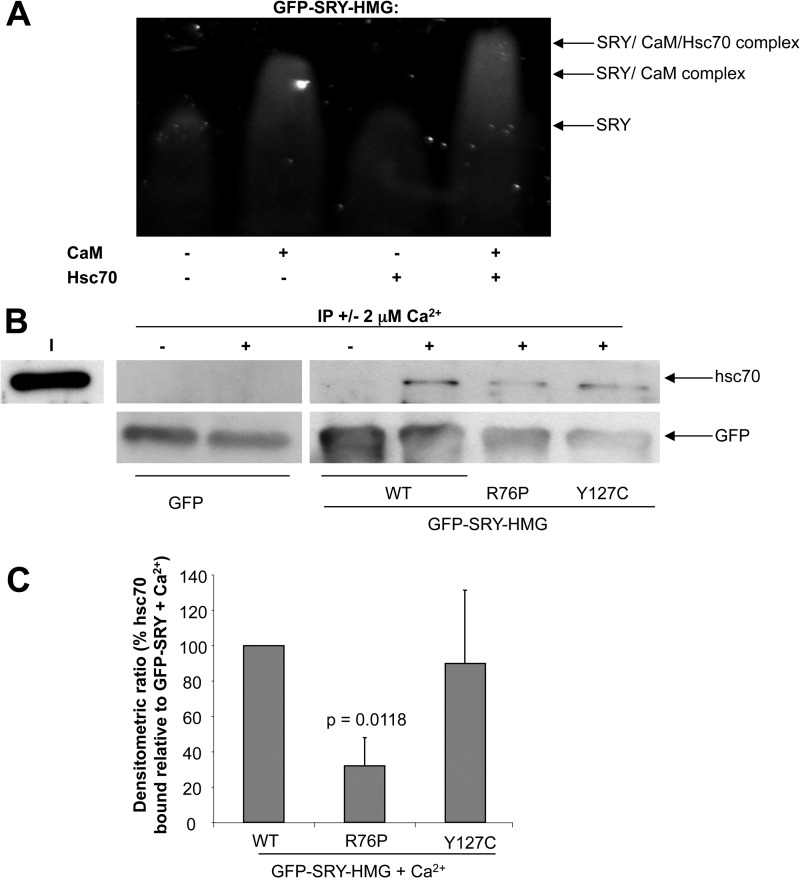
FIGURE 3.
hsc70 specifically binds the SRY/CaM complex in Ca2+-dependent fashion. A, native PAGE gel mobility shift assay (see “Experimental Procedures”) for hsc70 and CaM binding to GFP-SRY-HMG (wild type) was performed, where GFP-SRY-HMG (1 μm) was incubated in the absence and presence of hsc70 (1 μm) and/or CaM (1 μm) in the presence of Ca2+ (2 mm) for 20 min at room temperature as indicated, and then fluorimaging was performed subsequent to gel electrophoresis. Results are shown for a single typical assay from a series of three similar experiments, with SRY·CaM and SRY·CaM·hsc70 complex formation indicated on the right. B, immunoprecipitation using GFP-TRAPTM resin was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures,” with immunoblots probed with anti-GFP or anti-hsc70 antibodies to detect binding of GFP or GFP-SRY-HMG wild type and NLS mutant derivatives in the absence and presence of 2 μm Ca2+ as indicated to hsc70. I, input. C, densitometric analysis for immunoprecipitation assays was performed on images such as those in B for hsc70 binding to the GFP-SRY-HMG and NLS mutant derivatives in the presence of Ca2+, as indicated. Results represent the mean ± S.E. (n = 3) of the percentage hsc70 bound relative to GFP-SRY in the presence of Ca2+, with p values shown where there were significant differences compared with wild type.