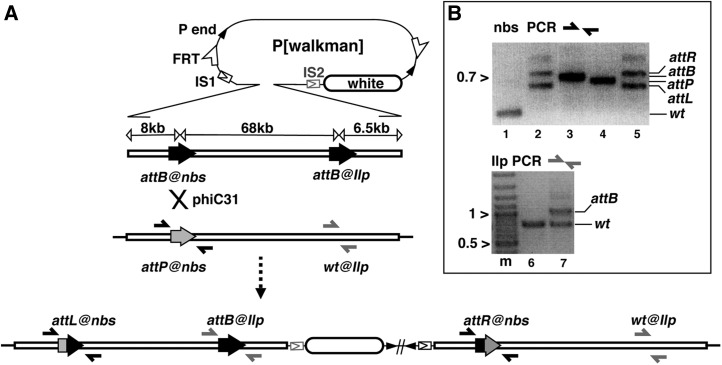
Figure 1 .
Generating an 80-kb duplication by site-specific integration. (A) Integration schematic. At the top is the pWalkman vector built on the pP[acman] backbone, which contains P-element ends (solid arrowheads), a white maker (open oval), FRT sites (half-arrows), and an I-SceI cut site (IS1 in construct pWalkman{nbs-Ilp} IS1 and IS2 in pWalkman{nbs-Ilp} IS2). Below the pWalkman vector is the 82-kb nbs-Ilp insert, which contains two attB sites (solid arrows), one at each locus, separated by 68 kb. Below the 82-kb insert is the chromosomal region with an attP (shaded arrow) targeted to nbs. Note that the chromosomal region of Ilp does not contain any att site (wt). The positions for two sets of PCR primers (solid and shaded half arrows) used in B are indicated. A phiC31-mediated recombination (“X”) between attP and attB at nbs gives rise to the duplication depicted at the bottom. Only the integration of pWalkman{nbs-Ilp}IS1 is shown. The FRTs are not shown but are in close proximity to the P-element ends. (B) Representative results for diagnostic PCR tests. Marker size in kilobases is indicated to the left of the gel images. (Top) PCR analyses with nbs primers. The PCR templates are the following: lane 1, a wild-type line without any attachment site; lane 2, a duplication line from previous plasmid integration at attP@nbs; lane 3, plasmid DNA of pWalkman(nbs-Ilp)IS1; lane 4, the attP@nbs starting line; and lane 5, an integration line with the 80-kb duplication. (Bottom) Results of PCR analyses with Ilp primers. Lane “m” contains the marker. The PCR templates are the following: lane 6, a wild-type line, and lane 7, an integration line from this study.