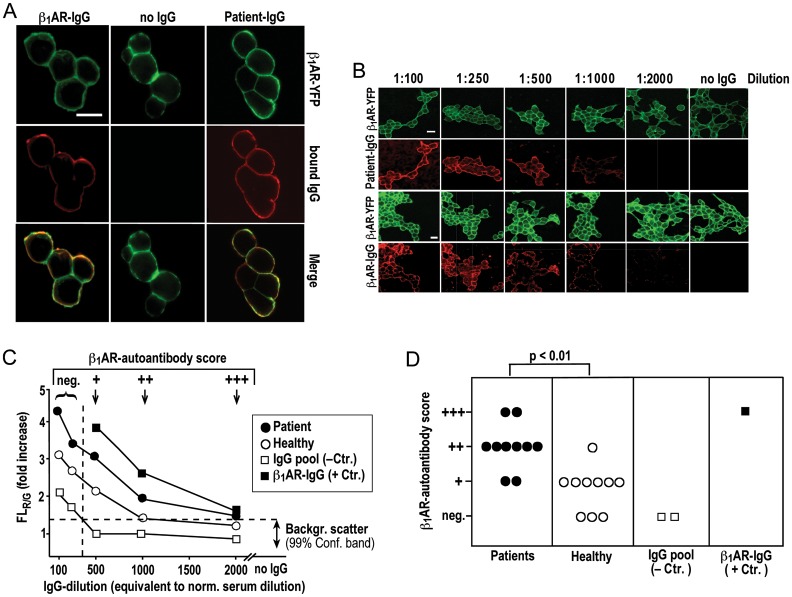
Figure 1.
Colocalization of IgG with native YFP-fused β1AR on the surface of human cells. (A) Colocalization (bottom) of β1AR- (top) and IgG-associated fluorescence (middle) on native cells incubated with IgG (26.8 mg/L) from a DCM patient (right), secondary antibody alone (middle) or rabbit β1AR-IgG (left); visualization at 630-fold magnification, size bar (30 μm) at top left applies to all panels. (B) Serial dilution of patient IgG (top) or rabbit β1AR-IgG (bottom) starting with 134 mg IgG/L (equivalent to 1:100 dilution of normal serum); green and red images show receptor- and IgG-associated fluorescence, respectively, at 200-fold magnification. Size bar (30 μm) at top left applies to all panels. (C) Cells stained with serial IgG dilutions and imaged as in (B); the ratio of emission intensities of red (bound IgG) and green (β1AR abundance) fluorescence intensities (FLR/G) is normalized to FLR/G background with second antibody alone. FLR/G increases above background (mean values from 10 fields of vision, SEM <20% not shown) are plotted over dilution of IgG from a DCM patient (filled circle), a healthy volunteer (open circle), a commercial human-IgG preparation (open square) or rabbit antibodies against the second extracelluar loop of the human β1AR13 (filled square). Horizontal dashed line: confidence limit of FLR/G background scatter (determined in 10 independent cell preparations, 30 fields of vision each). Vertical dashed line: specificity cut-off. (D) Scoring of β1AR autoantibody positivity [criteria at the top of (C)]; means of triplicate determinations of individual IgGs done on different days with different cell preparations; SEM was less than one dilution step; Bracket: U test.