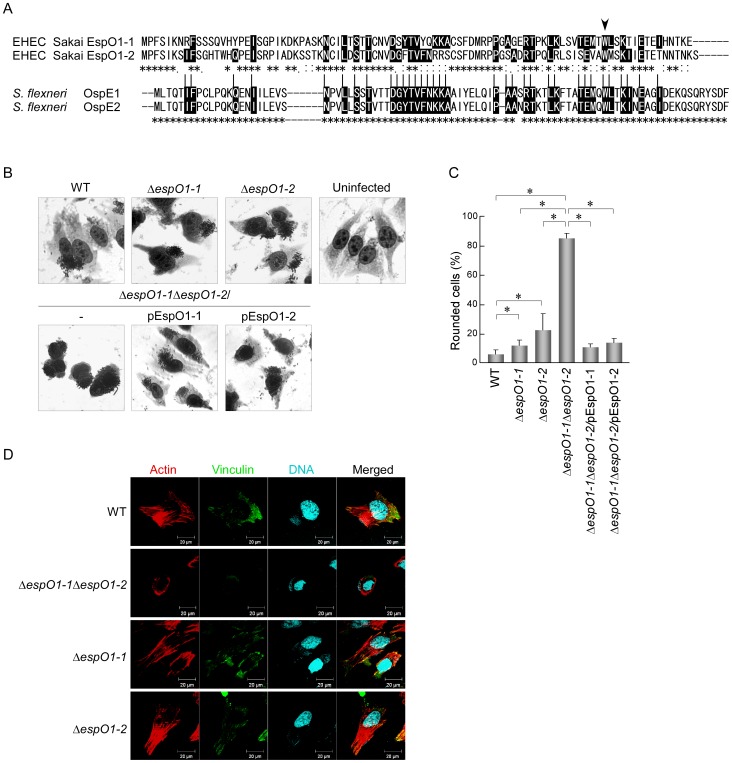
Figure 1. EspO1-1 and EspO1-2 stabilize FAs and the actin cytoskeleton in EHEC-infected cells.
(A) Alignment of OspE2 homologs EspO1-1 and EspO1-2 in EHEC strain Sakai. EspO1-1 and EspO1-2 have 59% amino-acid sequence identity, and also have extensive homology with OspE2 (29% and 25% amino acid sequence identity to OspE2, respectively). Asterisks indicate amino acid residues that are conserved in either OspE1 and OspE2 or in EspO1-1 and EspO1-2. Black highlight indicates an amino-acid residue conserved in both OspE1 and OspE2 and either EspO1-1, EspO1-2, or both EspO1-1 and EspO1-2. Arrowhead indicates the tryptophan, which is involved in ILK binding, at amino acid residue 77 of EspO1s and residue 68 of OspEs. (B) Morphological change in HeLa cells uninfected or infected with EHEC. HeLa cells were infected with EHEC wild-type (WT), an ΔespO1-1 mutant (ΔespO1-1), an ΔespO1-2 mutant (ΔespO1-2), an ΔespO1-1ΔespO1-2 double mutant (ΔespO1-1ΔespO1-2), an ΔespO1-1ΔespO1-2/pEspO1-1 or an ΔespO1-1ΔespO1-2/pEspO1-2. At 4 h post-infection, the cells were fixed and Giemsa-stained. (C) Percent cell rounding in cells infected by WT, ΔespO1-1ΔespO1-2, ΔespO1-1 or ΔespO1-2 shown in (B) and quantified (>50 cells, n≥3). Data are the mean and S.D. *P<0.001. The percent of cell rounding of uninfected cells was <3%. (D) Formation of actin filaments and focal adhesions (FAs) in HeLa cells infected with EHEC. HeLa cells were infected with WT, ΔespO1-1ΔespO1-2, ΔespO1-1 or ΔespO1-2. At 4 h post-infection, the cells were fixed and processed for confocal laser scanning microscopy using rhodamine-phalloidin to visualize actin filaments (red), anti-vinculin antibody to visualize FAs (green), and DAPI to visualize DNA/chromosomes (blue).