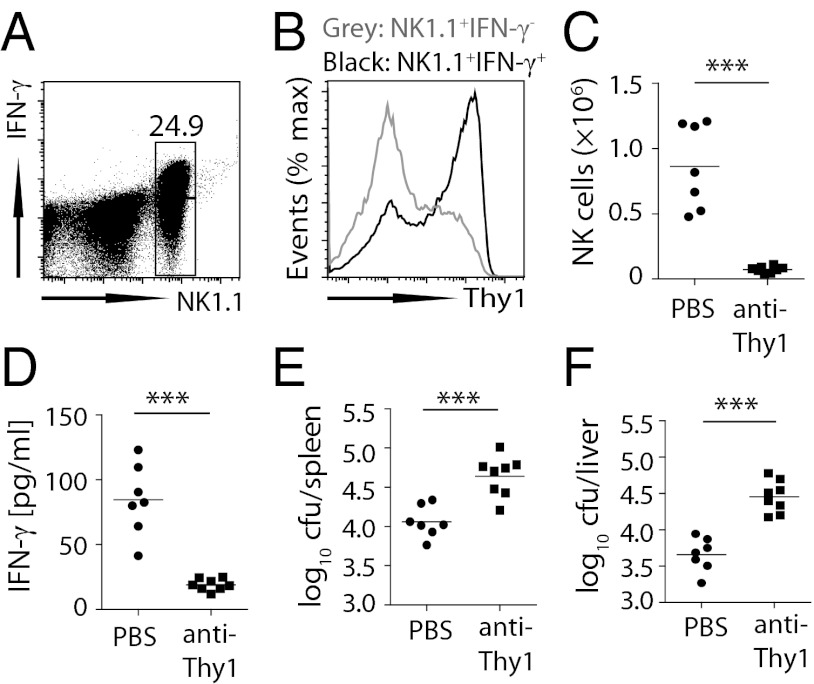
Fig. 3.
Thy1+ NK cells produce IFN-γ and contribute to Salmonella control. (A and B) Rag1/Je−/− mice were injected i.v. with 1 × 108 cfu heat-killed S. Typhimurium (HKST), and IFN-γ secretion by CD3−NK1.1+ cells was assessed 2 h later in the spleen (A). IFN-γ+ (black) and IFN-γ− (gray) NK 1.1+ cells were assessed for expression of Thy1 (B). (C–F) Rag1/Je−/− mice were treated i.p. with PBS or anti-Thy1 (30H-12) and infected i.v. with 200 cfu S. Typhimurium BRD509 48 h later. Injection of depleting antibodies was continued twice weekly for 3 wk. Bacterial numbers in spleen (E) and liver (F), serum IFN-γ levels (D), and NK cell numbers (C) were assessed on day 21 after infection. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Representative FACS plot (A) and histogram (B) or individual data points (C–F) are shown. Statistical analysis: paired Student t test. ***P < 0.001.