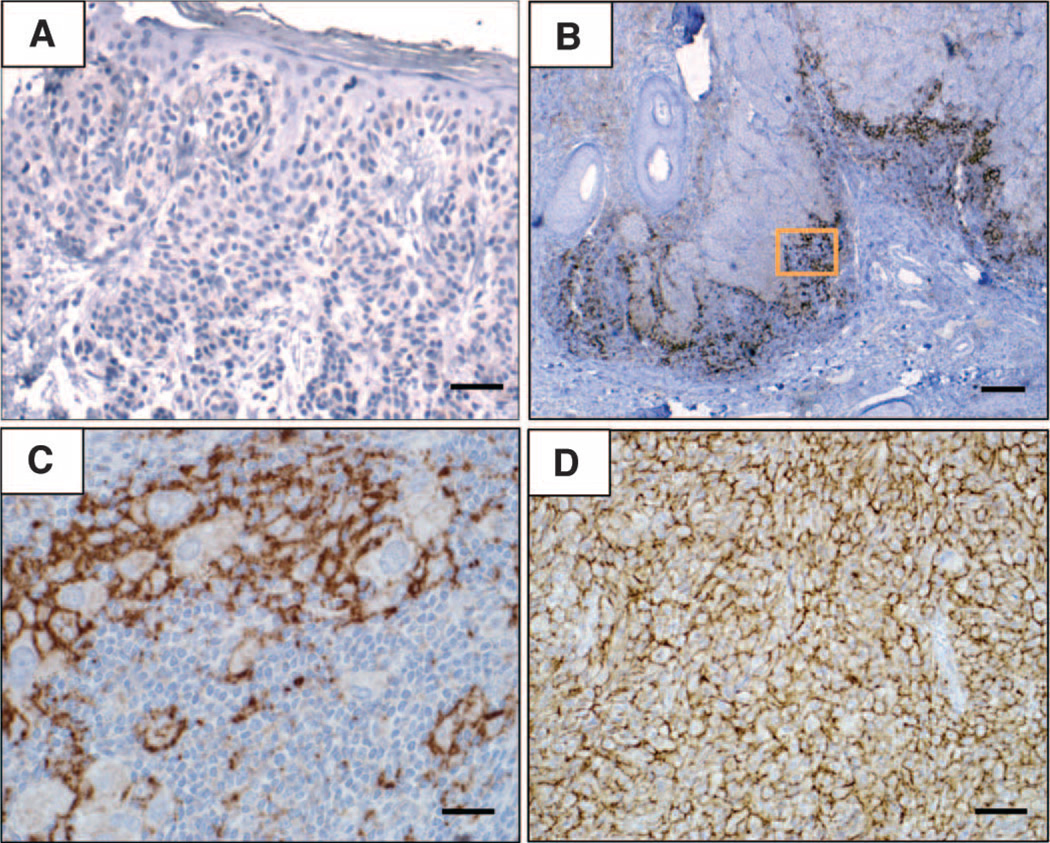
Fig. 1.
Patterns of B7-H1 expression observed in melanocytic lesions stained with the anti–B7-H1 mAb 5H1. (A) No B7-H1 expression (brown chromogen) by melanocytes in a benign nevus. Original magnification, ×200 (scale bar, 50 µm). Note the paucity of TILs in this case. (B) B7-H1 expression by both melanocytes and TILs at the advancing edge of an invasive primary melanoma, nodular histologic subtype. Original magnification, ×40 (scale bar, 200 µm). (C) Original magnification of the boxed area shown in (B), ×400 (scale bar, 20 µm). Overall, 10% of total melanoma cells in this specimen expressed B7-H1 (scoring was performed as described in Materials and Methods). The inflammatory host response to tumor was graded as “moderate” in this case and included B7-H1+ TILs. (D) Diffuse B7-H1 expression by melanocytes in a subcutaneous melanoma metastasis to the scalp, associated with singular TILs. Original magnification, ×200 (scale bar, 50 µm). Representative photomicrographs of CD3 staining for TILs corresponding to each of these examples are shown in fig. S1. The interface pattern with B7-H1 expression by both melanocytes and TILs at the advancing edge pre-dominated in this study.