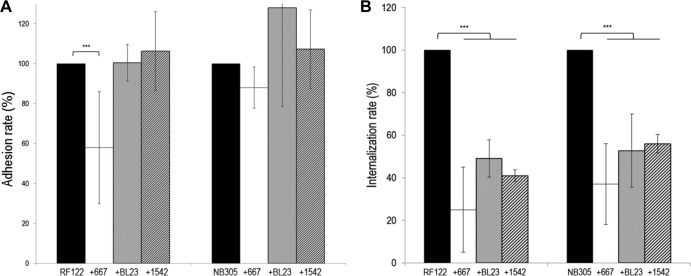
Fig 4.
Inhibition of adhesion and internalization of S. aureus RF122 and NB305 by L. casei strains. (A) Rates of adhesion of S. aureus RF122 and NB305 strains to bMEC following preincubation of cells with L. casei CIRM-BIA 667 (white bars), BL23 (gray bars), and CIRM-BIA 1542 (hatched bars) at an ROI of 2,000:1. (B) Rates of internalization of S. aureus RF122 and NB305 into bMEC in the presence of L. casei CIRM-BIA 667 (white bars) and BL23 (gray bars) at an ROI of 2,000:1 and CIRM-BIA 1542 (hatched bars) at an ROI of 400:1. Adhesion and internalization assays were performed with an S. aureus MOI of 100:1. Adhesion/internalization assays of S. aureus alone were used as a reference (black bars). Adhesion/internalization rates were then defined as the adhered/internalized S. aureus population in the presence of L. casei relative to the adhered/internalized S. aureus population in the reference experiment. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations. Each experiment was done in triplicate, and differences between groups were compared using Student's t test with Bonferroni's correction. ***, P < 0.0005.