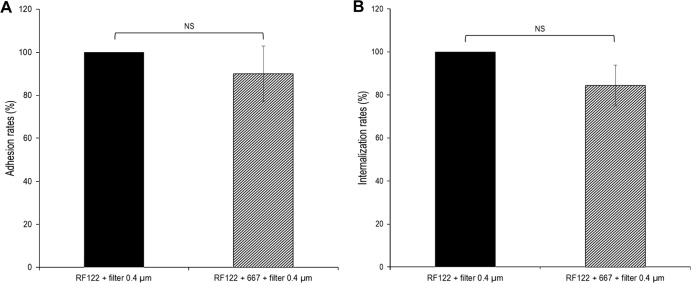
Fig 8.
L. casei inhibition of S. aureus adhesion and internalization requires contact with bMEC and/or S. aureus. Adhesion and internalization assays were performed, as previously described (see the legends to Fig. 2 and 3), using S. aureus RF122 at an MOI of 100:1 and L. casei CIRM-BIA 667 at an ROI of 2,000:1, except that L. casei was separated from S. aureus and bMEC using a cell culture insert. Adhesion/internalization assays of S. aureus alone with the cell culture insert were used as references. Adhesion/internalization rates were then defined as the adhered/internalized S. aureus population in the presence of L. casei relative to the adhered/internalized S. aureus population in the reference experiment. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations. Each experiment was done in triplicate, and differences between groups were compared using Student's t test. NS, not significant.