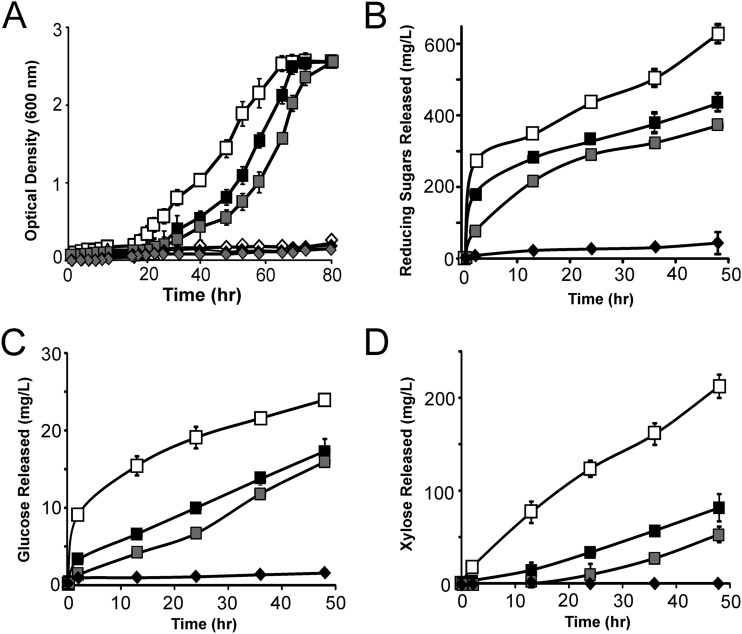
Fig 6.
Cells displaying minicellulosomes containing three enzymes grow on untreated corn stover, straw, and switch grass. (A) Growth curves of minicellulosome-displaying B. subtilis cultured with untreated corn stover (open squares), straw (solid squares), and switch grass (shaded squares). In each assay, cells were grown on M9 salts and 0.5% (wt/vol) untreated biomass. Strain TDA18, which only secretes the enzymes, could not grow on corn stover (solid diamonds), straw (shaded diamonds), or switch grass (open diamonds). (B) Reducing sugars released by minicellulosome-displaying azide-treated cells (strain TDA17). Sugars released from corn stover (open squares), switch grass (shaded squares), and straw (solid squares) are shown. Solid diamonds are data from control strain TDA18 cultured with untreated corn stover, which produced only small amounts of soluble sugar (similar data, not shown, were obtained with straw and switch grass). (C) Data are identical to those shown in panel B but report the concentration of soluble glucose released from untreated biomass. (D) Data are identical to those of panels B and C but report the concentration of soluble xylose released.