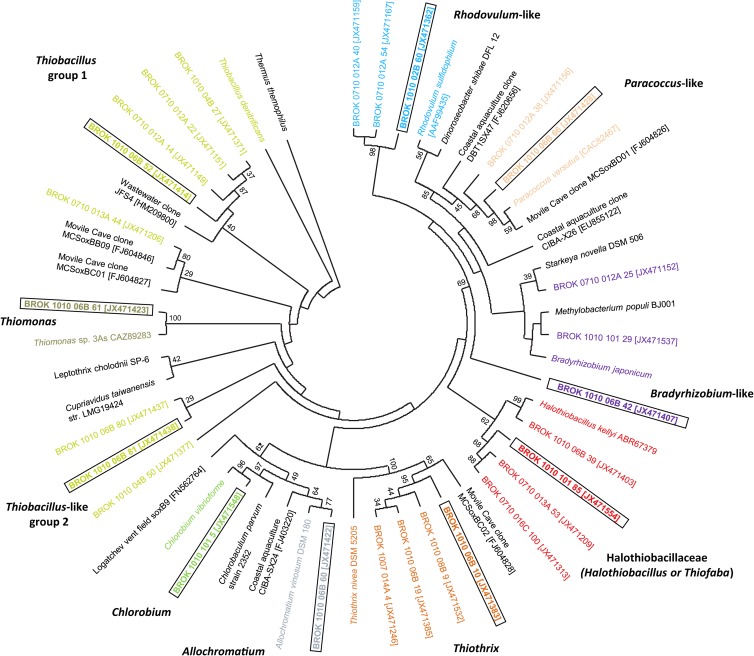
Fig 3.
Phylogenetic tree of translated soxB sequences from clones that represent distinct OTU groups obtained from Rattlesnake Spring. Taxonomic identification for each of the OTU groups is color coded for comparison to Fig. 2 and 4. Accession numbers for clones from this study, environmental clones previously identified from other investigations, and cultured isolates are shown in brackets. Topology was inferred using maximum likelihood under the WAG+G+I+F method for amino acid substitution (G = 1.69, I = 0.01, and F = 0.081). Bootstrap values of major branch points are shown.